A guide to enhancing security, efficiency and scalability
Introduction to IoT in the Public Sector
The Rapid Growth of IoT in Public Services
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionising how public sector organisations operate. From smart cities to healthcare, traffic management, environmental monitoring, and social housing, IoT devices are everywhere and enhancing public services by enabling real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and optimised resource management. This leads to greater operational efficiency, cost savings, lower environmental impact, and improved service delivery.
The Challenge of Security and Management
IoT devices offer unparalleled benefits. However, with the rapid expansion of IoT networks comes an increased need for robust security measures. As public sector organisations deploy more connected devices, they face significant challenges in securing these networks from cyber threats, with the number and variety of attacks increasing exponentially. Ultimately, any IoT device is only as secure as the network that it operates over!
Scalability is another concern. Traditional methods of network deployment for large-scale IoT projects, such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), often lead to configuration becoming increasingly time-consuming and complex, with IT teams struggling to manage a sprawling network of interconnected devices.
To address these challenges, ensure network security and data privacy, and manage the scalability of IoT deployments, it is therefore crucial to understand the evolving threat landscape and consider strategic network solutions that provide both security and flexibility.
The Cyber Threat Landscape for IoT Deployments
Understanding the Evolving Cyber Threats
As the adoption of IoT devices grows, so do the associated cybersecurity risks. According to the SonicWall Cyber Security report, there has been a 107% increase in attacks targeting IoT devices in the first half of 2024. IoT devices connected to the public internet may provide cybercriminals with a significant attack surface through which to exploit vulnerabilities in devices, such as default passwords and unpatched firmware, and subsequently execute DDoS attacks, data breaches, and ransomware attacks.
The Impact on Public Sector Organisations
For public sector entities dealing with sensitive data and critical services, the consequences of a security breach can be severe, including operational disruptions, loss of public trust, financial costs, and legal repercussions. It is essential to identify these vulnerabilities and adopt effective strategies to protect IoT networks from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Traditional Approaches to Securing IoT Networks and Their Limitations
Traditional Security Methods
Integrating IoT devices on traditional networks generally requires intricate configurations to ensure data privacy and compliance with regulatory standards. While it is possible to secure devices using Carrier-Grade NAT to translate from a private to a public IP address, this is only suitable where a device initiates the transmission and not where remote access is required for management and updates. In this case, a public IP address is needed, which then leaves the device open to attack.
As a result, secure networks are often implemented using encryption algorithms and IP Sec VPN tunnels, making it more difficult for unauthorised parties to access or intercept sensitive information. Regularly reviewing and updating the network configuration and security settings is required to ensure all components are operating with the most current security protocols. The network may also be divided into smaller, manageable segments so that potential breaches can be isolated and stopped from spreading.
While these methods provide a certain level of security, they also come with significant drawbacks:
- Scalability Issues:
- As the number of IoT devices grows, managing and configuring VPNs becomes exponentially more complex and time-consuming, making it difficult to scale efficiently.
- Operational Issues:
- The requirement for continuous monitoring and rapid response capabilities can strain an organisation’s operational capacities.
- High Costs:
- The depletion of IPv4 addresses has led to higher costs for public IP addresses. Additionally, VPN setups increase hardware and maintenance expenses.
- Security Risks:
- Direct exposure to the public internet makes devices vulnerable to unauthorised access, breaches, and attacks.
The Need for a New Approach
Given these limitations, public sector organisations need to explore more secure, scalable, and cost-effective alternatives that address the challenges posed by traditional network security methods.
The Advantages of a Private Network Solution for Secure IoT Connectivity: An Overview of Spitfire’s One Network
Introducing Private Network Solutions for IoT
Private network solutions, like Spitfire’s One Network, offer a modern approach to IoT connectivity by keeping devices hidden from the public internet and minimising the risk of unauthorised access. Rather than using public IP-based solutions with their associated vulnerabilities, a private network places all connected devices within a secure, protected network environment.
Spitfire’s One Network: A superior solution
Spitfire’s One Network offers a transformational solution for connecting, monitoring, and managing any size estate of IoT devices. A fully private network, it eliminates traversal of the public internet, significantly reducing exposure to cyber threats and shielding sensitive data from interception or unauthorised access.
Until now, deploying a robust IoT solution has usually called for multiple connectivity supplier relationships involving complex integrations and management, with the added vulnerability of data traversing the public internet.
One Network seamlessly integrates mobile, fixed-line, and cloud connectivity into a unified, secure private MPLS network under a single end-to-end supplier relationship.
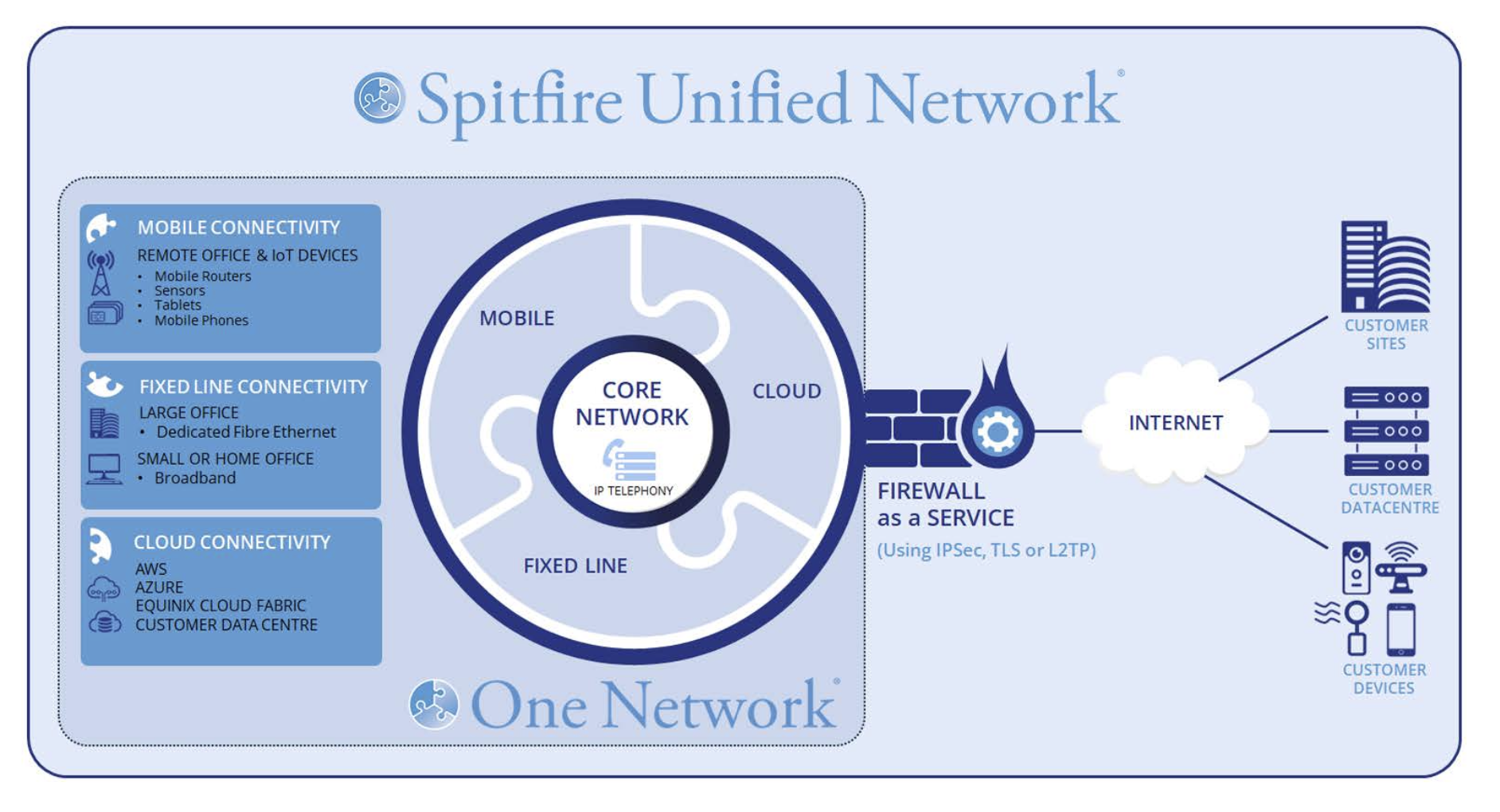
- Enhanced Mobile Connectivity:
- As a full MVNO we have complete control and flexibility over configuration, provisioning, pricing and support. With options for ‘home’ and multi-network, complete UK geographic coverage, redundancy, and diversity to ensure devices can connect securely from anywhere.
- Fixed Line and Cloud Integration:
- Seamless integration with fixed-line fibre circuits and cloud environments like AWS and Microsoft Azure, avoiding the need for data to traverse the public internet at any point within the network.
- Future-Proofing with IPv6:
- As the limitations of IPv4 become more apparent, Spitfire’s Enhanced Mobile configurations enable the use of private IP addresses while supporting the transition to IPv6 for more scalable IoT networks.
Key Benefits of One Network:
- Enhanced Security:
- Devices remain off the public internet, significantly reducing the attack surface and the risk of any unauthorised access.
- Operational & Cost Efficiency:
- It eliminates the need for multiple public IP addresses, network configuration, and maintenance, lowering operational expenses.
- Scalability and Simplicity:
- Simplified management and faster network deployment with potentially no configuration required by the end-user, allowing for easy scaling with minimal hardware requirements and reduced data overheads.
- Sustainability:
- The ability to deploy devices with less powerful processors and lower energy consumption aligns with many organisations’ sustainability goals.
Aligning with Public Sector Requirements
These features align perfectly with the needs of public sector organisations, which require secure, compliant, and scalable network solutions to handle sensitive data and critical operations effectively.
Real-World Applications in the Public Sector
Use Case 1: Environmental Monitoring in Social Housing
Local councils are deploying IoT sensors to monitor conditions like mould and dampness in social housing. A private network approach ensures that these devices are managed securely, protecting sensitive data while enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Use Case 2: Healthcare
Healthcare organisations use IoT devices for real-time patient monitoring, asset tracking, and data management. A private network provides the secure, low-latency connectivity needed to protect patient data, comply with privacy regulations, and improve patient care without risking compliance breaches.
Use Case 3: Smart Cities & Buildings
Councils and local authorities use IoT sensors for various applications, including refuse collection, environmental monitoring, and smart traffic systems. The security of these systems is paramount, and a private network like One Network provides the needed protection against cyber threats while optimising service delivery and operational efficiencies.
Benefits of Adopting a Private Network Solution
When considering IoT networks and their data connectivity requirements, public sector IT leaders and decision-makers should consider adopting private network solutions, like Spitfire’s One Network, for their future IoT deployments.
By shifting to a private network solution, organisations can ensure enhanced security, improved operational efficiencies, cost savings, and better service delivery in these and other use cases.
Further Reading & Information
- Healthcare Networks in the Age of IoT
- Beyond the Surface. Overcoming the Vulnerabilities of IP-based Security
- In-Depth look at IoT: Market Trends and Security
- One Network – Redefining IoT Connectivity
- Spitfire’s Full MVNO Launch – A New Era in Connectivity


