Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home Search
chemotherapy - search results
If you're not happy with the results, please do another search
Scientists create a test to predict chemotherapy resistance in patients
Scientists have developed a test which successfully predicts whether cancer will resist common forms of chemotherapy treatment.
A novel approach to cancer chemotherapy
Richard F. Ludueña, Professor Emeritus at the University of Texas Health San Antonio, discusses his innovative approach to cancer chemotherapy, which could significantly enhance its effectiveness.
New target to combat chemotherapy resistance in deadly brain cancer
For patients battling glioblastoma, a highly aggressive and deadly form of brain cancer, resistance to chemotherapy remains a significant obstacle.
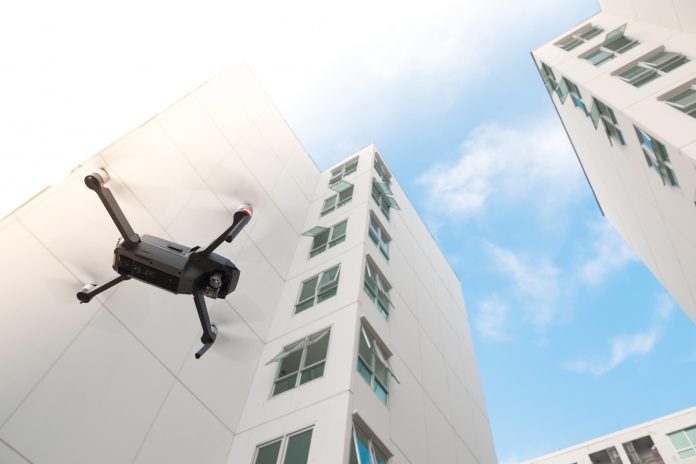
Drone chemotherapy becomes an NHS net zero cancer strategy
NHS cancer patients will be the first to experience drone chemotherapy, which furthers the NHS net zero strategy, as it cuts down travel time and distance.
Ordinary drug could prevent heart damage from breast cancer chemotherapy
Damaged heart muscle is a tragic possibility for patients of breast cancer chemotherapy - but thanks to Dr Husam Abdel-Qadir, there may now be a way to stop it.
US healthcare: Black people less likely to receive lung cancer chemotherapy
Boston Medical Center researchers found that Black individuals, above all other racial groups, are less likely to receive lung cancer chemotherapy.
Scientists discover way to protect hair from chemotherapy
Scientists have determined a new way to protect the hair follicle from chemotherapy in an effort to prevent hair loss as a result of cancer treatments.
Publishing national chemotherapy data
Publishing national chemotherapy data has helped NHS hospitals make changes that should improve treatment, as Emma Saxon reveals in this article
Scientists reveal new vaccine for recurring yeast infections
University of Georgia researchers have successfully created a vaccine that protects and treats vaginal yeast infections in mice.
Interactions between Microbiomes, Viruses, and Cancer
The University of South Florida and Tampa General Hospital Cancer Institute launches the “Microbial Oncogenesis and Cancer Therapy” consortium.
Breakthrough in treating aggressive breast cancer improves patient survival
A new treatment approach for aggressive breast cancers significantly improves survival rates for patients.
New grant targets hidden heart damage in cancer patients
A team of researchers from King's College London has been awarded £850k to develop imaging tests that detect heart damage caused by cancer.
Faster cancer diagnoses reduce wait times for 80,000 patients
The UK government’s £26 billion NHS investment has enabled 80,000 more people to receive cancer diagnoses or all-clear results within 28 days.
WHO issues first-ever report on invasive fungal diseases
The World Health Organization (WHO) has published its first-ever report addressing the lack of medicines and diagnostic tools for invasive fungal diseases.
£5.5 million pledged to transform bowel cancer care
Research institutes have committed £5.5 million in funding for a world-leading research team tasked with making personalised medicines for bowel cancer patients.
First-ever NHS treatment approved for advanced Hodgkin lymphoma
New combination therapy will be available on the NHS, offering new hope to people with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma.
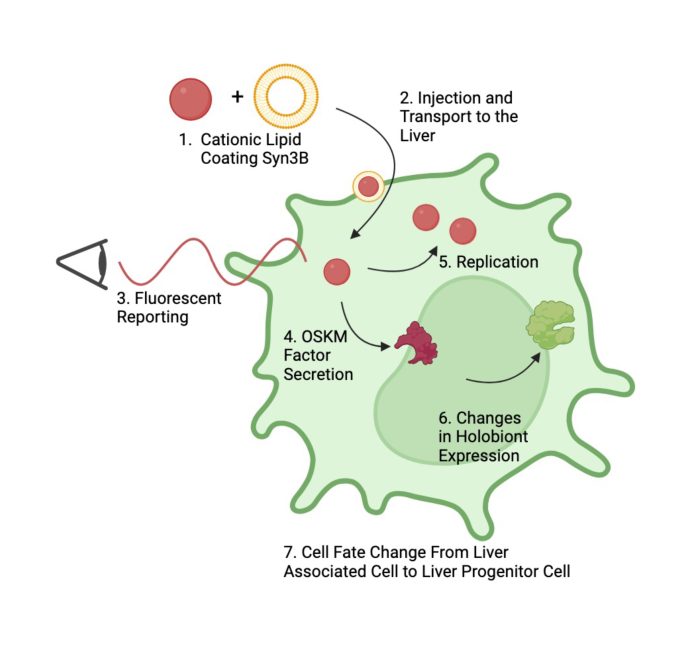
Tracing evolution’s blueprint: Minimal genome life and the engineering of synthetic endosymbiosis
Roksana Riddle and Christopher H. Contag from Michigan State University discuss the concept of endosymbiosis, how it has evolved, and present strategies to engineering endosymbionts and their applications in developing innovative therapies.
CYP genes and haplotypes in personalised medicine
Brian Tait, Chief Scientific Officer at Haplomic Technologies Pty Ltd, focuses here on CYP genes, haplotypes, and their applications in personalised medicine.
Reducing oxidative stress: Antioxidants key in the fight against non-communicable diseases
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) thrive on oxidative stress, an imbalance of reactive oxygen species. This review delves into the crucial interplay between antioxidant enzymes and dietary antioxidants.
Could medical imaging innovation be the catalyst for precision medicine?
We all have a unique face, fingerprint, voice, and signature, so why wouldn’t we have a unique response to the medicine and treatments we receive? Mark Hitchman, Managing Director at Canon Medical Systems UK, explores this question.