Optimising a drug’s ability to reach diseased body parts in adequate levels while avoiding healthy body parts – its tissue exposure and selectivity – is critical to therapeutic optimisation
Targeted drug delivery has been the Holy Grail of the pharmaceutical industry for decades. Managing many diseases remains challenging due to suboptimal penetration of systemically administered therapeutic drugs, such as chemotherapies, targeted small molecules, and antibodies. Systemic administration results in therapy distributing to normal healthy tissue, often inducing toxic effects that can severely limit the doses that can be applied.
Scientists have paid particular attention to externally activated drug delivery systems, such as the use of heat, light, ultrasound, and electric and magnetic fields as external energy sources to activate various drug formulation systems to enhance extravasation and distribution of a systemically co-administered drug. There has been significant interest in utilising ultrasound and microbubbles which couple strongly to the ultrasound fields to drive targeted therapeutic amplification in recent years. Low-intensity ultrasound in combination with microbubbles has been shown to increase the vasculature’s permeability safely and transiently, allowing more drug to reach the target pathology.
Norwegian clinical-stage company, EXACT Therapeutics AS, is enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of medicines with its novel ultrasound-mediated drug delivery technology platform called Acoustic Cluster Therapy (ACT®).
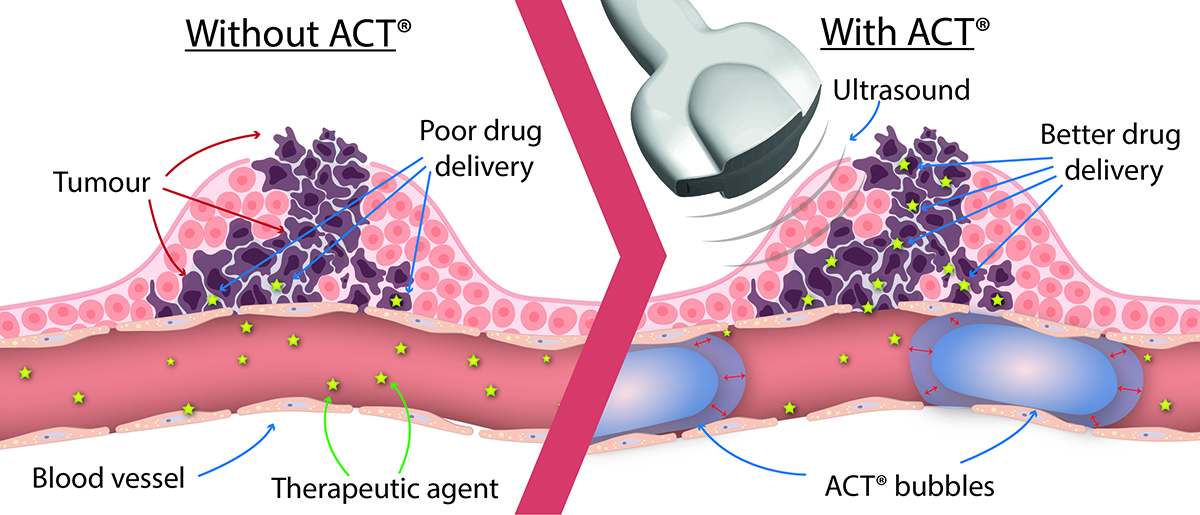
Ultrasound and ACT® for targeted drug delivery
Microbubbles have been used as imaging contrast agents for decades in a diagnostic setting with ultrasound with an excellent safety profile based on the inert nature of the formulations available. Ultrasound itself is well established in the medical environment including in developing countries, and ACT® is positioned as an add-on without negatively affecting or interfering with therapeutic treatment. Furthermore, the near ubiquitous availability of ultrasound systems in healthcare settings worldwide provides a strong foundation for the future potential and adoption of ultrasound for therapeutics increasing the impact of precision health across geographies.
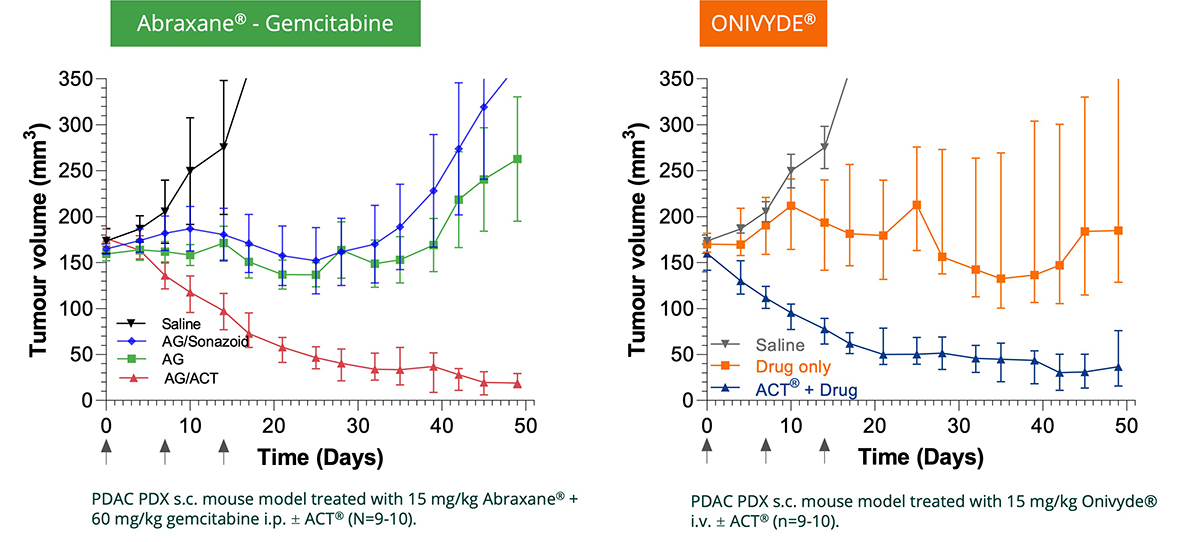
The power of Ultrasound technology
Ultrasound can also be used outside diagnostic applications to induce local biological effects deep inside the body without surgical intervention allowing spatially specific delivery at desired sites. Combining with microbubbles, ultrasound has shown to enhance drug uptake in a target volume such as tumours.
The ACT® platform is supported by a strong and broad preclinical package demonstrating therapeutic enhancement in multiple oncology models (pancreatic, breast, colon, and prostate), in infectious foci, and to enable controlled blood-brain barrier (BBB) opening with a strong safety profile.
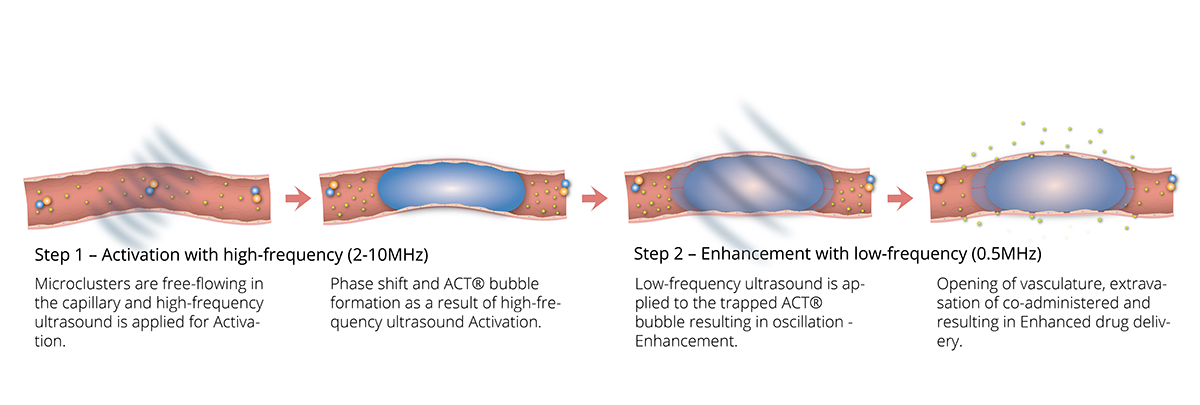
The ACT® bubble
The proprietary ACT® formulation consists of negatively charged microbubbles and positively charged microdroplets and it is co-administered with a therapeutic agent. These highly engineered small (<5μm) microbubble- microdroplet clusters are free flowing in the bloodstream like regular contrast agents before insonation.
The ACT® formulation is optimised to achieve its therapeutic benefit through a two-step ultrasound process. Following the intravenous injection of the ACT® formulation, high-frequency ultrasound is then applied to the target site allowing the microbubbles to transfer acoustic energy to the attached droplets which undergo a liquid-to-gas phase shift, called the Activation Step. Resulting vapor bubbles rapidly expand and get trapped in the next capillary bed they flow into, transiently stopping blood flow for up to 10min. Further application of low-frequency ultrasound, called the Enhancement step, oscillates the bubbles in a controlled manner and induces mechanical effects such as microstreaming and shear stress on the capillary wall that increase the local permeability of the vasculature and improve the transport of the co-administered therapy across the capillary wall and through the extracellular matrix (ECM).
It is important to note that the standard microbubbles have a typical diameter of 2-6 μm and are free flowing, while the ACT® bubbles are up to 3 orders of magnitude larger, allowing them to trap and temporarily lodge at the capillary level affecting a much larger part of the endothelial wall suggesting more efficient biomechanical effects on the capillary wall and the ECM. The approximately 5-10 times larger diameter ACT® bubble and its contact with a large part of the endothelial wall is thought to be critical for optimal targeted drug delivery and enhancement with ultrasound.
The ACT® platform is being developed for use with clinically approved diagnostic ultrasound scanners that are commonly found in hospitals and clinics worldwide. Currently, a Phase I Clinical Trial to investigate safety and toxicity has been initiated at Royal Marsden Hospital in London, treating colorectal cancer patients with liver metastases with standard chemo-therapy combined with ACT® (NCT04021277).
This localised drug delivery strategy that is minimally invasive and both drug and disease-agnostic is highly attractive as it could offer a much higher proportion of patients access to treatment and improved therapeutic outcomes.
References
Sontum P, Kvåle S, Healey AJ, Skurtveit R, Watanabe R, Matsumura M, et al. Acoustic Cluster Therapy (ACT)–A novel concept for ultrasound mediated, targeted drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2015; 495: 1019-27.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04021277
Please note: This is a commercial profile.
© 2019. This work is licensed under CC-BY-NC-ND.