Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home 2026
Archives
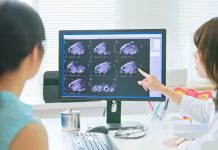
Magnetobiology: Beyond attraction
Jinxing Li and Christopher H. Contag delve into the emerging field of magnetobiology, which utilizes magnetic fields to manipulate and control living systems, while reflecting on its potential to surpass the limitations of other modalities.
Beyond microbial fermentation: Reimagining biomanufacturing for low-resource environments
Although traditional biomanufacturing is based on microbial or mammalian cell culture, plants can be grown in bioreactors and hold enormous promise for use in resource-limited environments.
Exploring genetic tools in environmental microbes: Applications in extracellular electron transfer
Arpita Bose and Zhecheng Zhang explore genetic tools in environmental microbes, citing applications in extracellular electron transfer/
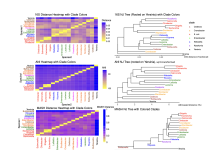
Lost in taxonomy: Why bacterial type strains are the anchor we need
Professor David Ussery and Dr. Ake Vastermark, bioinformatics and microbial taxonomy experts at Oklahoma State University, introduce the challenges of defining bacterial species in an era of rapidly expanding genomic data. Their article highlights how modern genome-based tools can bring clarity to this evolving field.
The benefits of harvest residue and vegetation control on conifer seedling survival and growth
Mark Kimsey, the Director of the Intermountain Forestry Cooperative, discusses the benefits of harvest residue and vegetation control on conifer seedling survival and growth.
Can stem cells aid coral reef recovery?
Shani Talice and Benyamin Rosental from Ben Gurion University of the Negev explore how stem cells could help corals recover from stress and environmental damage, addressing the urgent threats of climate change, pollution, and disease to coral reefs.
The science of gamification: Reimagining biomedical education through gamified learning
Dr Michael J. Dillon and Prof Laura Bowater examine the science of gamification to transform biomedical education through gamified learning.
Understanding botanical-drug interactions
With a specific focus on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic mechanisms, Dr Erin C Berthold discusses the interactions between botanical and herbal supplements and conventional pharmaceuticals, highlighting the urgent need to examine these interactions for public health and patient safety.
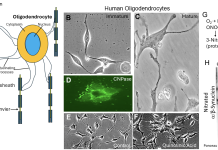
iPSCs and NSCs model newborn brain injury
This article discusses research by Dr. Lee J. Martin and his team on HIE, a leading cause of neonatal mortality. They use human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and neural stem cells (NSCs) and emphasize the vulnerability of oligodendrocytes, sharing how these cells can accumulate toxic misfolded proteins, potentially causing severe neural damage and long-term cognitive disabilities in affected infants.
Smarter decisions, better outcomes: How a new molecular test improves patient care
Oliver Bathe, Professor of Surgery and Oncology at the University of Calgary and CEO of Qualisure Diagnostics, examines how a new molecular test can lead to smarter decisions and better patient care outcomes in his third article.
Elimination of cervical cancer: Implementation in action
Professor Karen Canfell and Paul Grogan from the Cancer Elimination Collaboration at the Sydney School of Public Health discuss the WHO strategic plan for elimination of cervical cancer and how a combination of prevention, screening, and treatment can effectively achieve this goal.
Gut microbiome and aging – Unlocking new frontiers in healthy longevity
As the population ages, research into preserving healthy longevity is gaining pace. Christian Brechot highlights the role of the gut microbiome – a complex community of microorganisms within us – in influencing health as we age.
Bexyl Project: Beyond Xylella – Europe’s United fight against Xylella fastidiosa, a silent plant...
Across the Mediterranean, olive groves have shaped landscapes, cultures, and economies for centuries. But in the last decade, this heritage has come under threat from a silent plant killer: Xylella fastidiosa.
Vitamin a toxicity: “Too much of a good thing”
Fredric Gorin, Sarah Torres, and Pamela J. Lein discuss the implications of vitamin A supplementation during a recent measles outbreak in the US. They explain that a common misconception – that vitamin A supplementation can prevent the transmission of measles among unvaccinated individuals – can result in vitamin A toxicity.
Primate exposure to anthropogenic pollutants: Interactions with the gut microbiome and neuroendocrine SYSTEM
Michael Wasserman of Indiana University discusses interactions among the chemical exposome, microbes, and hormones in wild primates.
Understanding the role of botanicals in medicine
Dr Erin C. Berthold from Planted in Science Consulting LLC discusses the uses and perceptions of botanical medicines, emphasizing the necessity for coordinated global efforts to understand and regulate these substances to ensure their safe integration into healthcare.
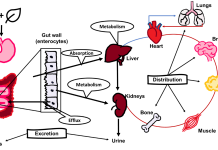
Enabling preventive medicine and improving patient care via aptamer-based molecular monitors
As health systems put greater focus on preventive, personalized care, Netzahualcóyotl Arroyo-Currás tells us about the broad benefits of Continuous Molecular Monitors (CMMs) in providing insights into biomolecular markers that facilitate early disease detection.
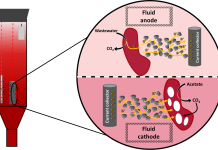
Purple phototrophic bacteria and microbial electrochemical technologies: A new biorefinery concept for wastewater treatment
The shift towards sustainable wastewater treatment focuses on nutrient recovery through biorefineries, highlighting the importance of microalgae, cyanobacteria, and, more recently, purple phototrophic bacteria for their metabolic flexibility and adaptability.
Raman spectroscopy for forensics: Identifying body fluid traces and gunshot residue
Here, the Department of Chemistry and the Center for Biophotonic Technology and Artificial Intelligence (CeBAI), investigates Raman spectroscopy for forensic applications, a universal technique for identifying traces of body fluids and gunshot residue.
The critical role of infection tolerance
Drawing on his research in understanding factors impacting infection tolerance, Brian P. Lazzaro, Liberty Hyde Bailey Professor at Cornell University, discusses the importance of tolerance to minor infections, highlighting that while active immune responses are crucial for pathogen defense, tolerance can often lead to better health outcomes.