Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home 2024
Archives
Modelling biodiversity is an essential part of its protection
Professor Guillaume Blanchet from Université de Sherbrooke considers why modelling biodiversity is an essential part of protection and how we can model biodiversity better.
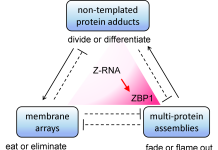
Cellular scaffolding: Crowdsourcing cellular responses in health and disease
In this article, Dr Alan Herbert discusses how different types of cellular scaffolds interact and impact the risk of diseases, citing the example of Z-RNAs pushing cells to inflammatory states in tumors and autoimmune conditions, setting the stage for new therapeutics.
The vital role of sustainable chemistry
Prof. Dr. Cecilia Van Cauwenberghe, PhD, MSc, BS, MBA, Research Director at Everest Group, sheds light on sustainable chemistry, including how breakthrough innovations drive global change.
A century of NAD+ insights drives aging science and solutions innovations
Dr. Rebecca Crews from Renue By Science, LLC, outlines a century of NAD+ insights driving aging science and, innovative solutions and much more.
Timely diagnosis and intervention for people with dementia
Jockey Club Centre for Positive Ageing experts highlight the importance of timely diagnosis and intervention for people with dementia.
Asbestos disease pathogenesis: The long and short of it
Jean Pfau and Kinta Serve explore a critical and novel hypothesis concerning the size of fibers in asbestos disease pathogenesis.
Catalysing vaccines and biologics manufacturing in Africa
Professor Faith Osier, Director of the Chanjo Hub at Imperial College London, shares her vision for vaccines and biologics manufacturing in Africa to secure lives and livelihoods and drive economic growth.
Harnessing hybrid molecules for drug development
Stoyanka Nikolova, Professor from Paisii Hilendarski Plovdiv University, discusses the potential of harnessing hybrid molecules for drug development and their possible application in addressing the clinical challenge of irritable bowel syndrome.
PETRI-MED: Enhancing marine phytoplankton diversity monitoring in the Mediterranean
Preserving biodiversity is crucial for sustaining life on Earth. Unfortunately, it is facing growing threats. Marco Talone and the PETRI-MED Team discuss their objectives for the PETRI-MED project and explain why it is urgently necessary.
Floreon technology, redefining polylactic acid
Dr Andrew Gill, CTO, and Dr Sandrine Garnier, CEO of Floreon Technology Ltd., explain how the company is redefining Polylactic Acid, starting with who they are and what they offer.
Protecting the human epigenome with nutritional epigenetics intervention programs
Dr Renee J. Dufault, Executive Director at the Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, explains the significance of nutritional epigenetics in understanding the impact of nutrients and dietary chemicals on gene expression patterns, as well as their role in the development of conditions such as autism and ADHD.
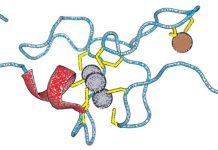
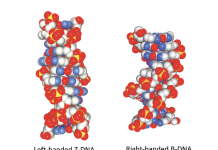
Flipons: The discovery of Z-DNA and soft-wired genomes
Alan Herbert, Founder and President of InsideOutBio, discusses alternative DNA conformations and understanding of their biological functions.
Extracellular electron transfer explained
Arpita Bose, PhD from Washington University in St. Louis, guides us through host-associated impacts and biotechnological applications of extracellular electron transfer in electrochemically active bacteria.
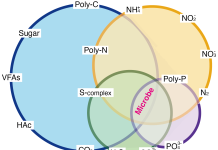
Microbes as high-potential green resource producers
Hui-Ping Chuang, Assistant researcher at the Sustainable Environment Research Laboratories of the National Cheng Kung University, shares insights into the vital role of microbes in waste removal and sustainable resource generation.
Fluorescent sensors for detecting anions
Nicola Edwards, Associate Professor of Chemistry at the University of St. Joseph, is conducting research on the development of fluorescent sensors for anion detection.
What imaging reveals about engineered endosymbionts
Ashley V. Makela and Christopher H. Contag from the Institute for Quantitative Health Science and Engineering, walk us through watching living therapeutics in action, including what imaging reveals about engineered endosymbionts.
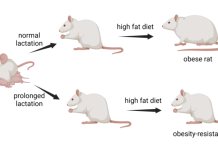
Prolonged lactation: Preventing obesity since infancy
Dr Vincent Prevot and Professors Markus Schwaninger and Ruben Nogueiras explain the significance of the perinatal maternal lifestyle, specifically prolonged lactation, in shielding offspring from chronic disease.
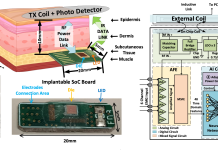
AI-empowered neural processing for intelligent human-machine interface and biomedical devices
Jie Gu, Associate Professor from Northwestern University, examines AI-empowered neural processing for intelligent human-machine interface and biomedical devices.
The different facets of biodiversity
Professor F. Guillaume Blanchet from Université de Sherbrooke explores the various aspects of biodiversity and the challenge involved in monitoring it.
Bacterial photobiohybrids and photosynthesis: Optimizing energy harvesting with bacterial-semiconductor hybrids
Photosynthesis serves as the primary mechanism for converting solar energy into chemical energy and plays a pivotal role in regulating atmospheric oxygen levels and carbon dioxide concentrations, influencing global climate patterns as a result.






![PETRI-MED: Enhancing marine phytoplankton diversity monitoring in the Mediterranean 1-day RGB composite image of the Mediterranean Sea as observed by Sentinel 3A and 3B on July 14th, 2022. ©EUMETSAT [2024] phytoplankton](https://www.openaccessgovernment.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/PETRI_MED_image-218x150.png)