Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home 2025
Archives
Screen time and myopia: Options for children’s vision in a digital world
With mounting evidence linking screen time to myopic progression, interest is growing in developing behavioral and nutritional vision care strategies to promote long-term ocular health in the digital age.
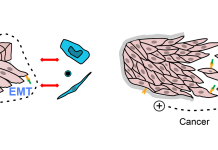
Cancers are like wounds because they are damaged tissue
Cancers resemble wounds. The question is why, and what does this mean? Many features of cancers – the so-called ‘Hallmarks of Cancer’ – may be mostly a wound-healing response. Dr Paul Edwards, Emeritus Reader at the University of Cambridge explores.
Rethinking papillary thyroid cancer: Why “low risk” isn’t always low impact
Oliver Bathe, Professor of Surgery and Oncology at the University of Calgary and CEO of Qualisure Diagnostics, urges us to rethink papillary thyroid cancer, noting that “low risk” isn’t always synonymous with low impact.
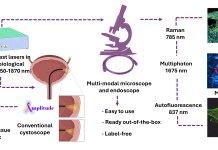
Novel imaging platform for early and precise cancer diagnosis
Regina Gumenyuk, Adjunct Professor at Tampere University, is exploring a novel imaging platform for early and precise cancer diagnosis. Read more about this exciting innovation here.
Personalized medicine in oncology: Small molecule inhibitors, biologics and immunotherapies
Priya Hays, PhD, CEO of Hays Documentation Specialists, discusses innovations and advancements in the development and evaluation of personalized cancer therapies.
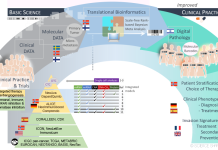
The European Cancer Pulse: From data intelligence to policy action
Norbert Couespel 1 and Mark Lawler 1, 2 highlight the European Cancer Pulse, a critical tool in tracking cancer inequalities and influencing cancer policy in Europe.
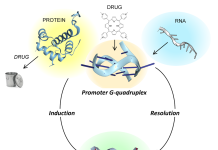
Targeting the most complex flipon of them all in the fight against cancers
In this article, Alan Herbert, the Founder, and President of InsideOutBio, guides us through targeting the most complex flipon of them all in the fight against cancers.
A novel approach to cancer chemotherapy
Richard F. Ludueña, Professor Emeritus at the University of Texas Health San Antonio, discusses his innovative approach to cancer chemotherapy, which could significantly enhance its effectiveness.
Fuelling the global supply of medical radioisotopes for cancer care
European research reactors play a crucial role in producing medical radioisotopes using nuclear fuel and are transitioning to Low Enriched Uranium (LEU) to meet non-proliferation commitments and global demand. Jared Wight tells us how he and his colleagues are working to ensure a smooth conversion to LEU fuels.
Breast cancer prevention: Precision medicine and health
Biobank Norway Project experts chart the journey from precision medicine to precision health when it comes to breast cancer prevention.
Protecting cancer survivors across Europe from financial discrimination: The right to be forgotten
Mark Lawler and Françoise Meunier highlight the financial discrimination that many cancer survivors face despite being cured of their disease and propose a data-informed legal solution so that cancer patients are not punished for a previous cancer diagnosis.
Artificial intelligence (AI) in mammographic screening in Norway
BreastScreen Norway discusses how the results from their screening programme for early breast cancer detection can influence future artificial intelligence to streamline early breast cancer detection.
From selfish silo to collaborative culture – embracing data-enabled cancer research
Aedin Culhane and Mark Lawler, Co-Leads of the eHealth Hub for Cancer, reflect on their data-enabled cancer research journeys, how their collaborative team science approach has reaped significant dividends in cancer research and policy and how the hub is inducing a paradigm shift in how health data are deployed on the island of Ireland.
Personalized cancer medicines
Dr. Priya Hays, PhD, CEO and Science Writer at Hays Documentation Specialists, LLC, guides us through the world of personalized cancer medicines.
T cells successfully fighting cancer
Else Marit Inderberg and Sébastien Wälchli from Oslo University Hospital explore what we need to know about T cells successfully fighting cancer.
Assessing blood clot risk in venous catheter selection for patients with haematological cancers
Venous catheters enable patients with haematological cancers to receive vital chemotherapy. However, there is a risk of thrombosis. Consultant Haematologist Priya Sriskandarajah analysed a group of patients with haematological cancers to study the implications of catheter selection.
The risk of malignant pleural mesothelioma
Although the use of asbestos-containing building materials was banned in the UK in 1999, this carcinogenic mineral continues to be a serious health threat. Daniel J. Murphy from the University of Glasgow tells us more.
Investigating lung cancer using genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMS)
Daniel J. Murphy, Professor of Lung Cancer & Mesothelioma at the University of Glasgow, School of Cancer Sciences, discusses opportunities for improving cancer research and care through the use of genetically engineered mouse models.
Are nanotextures enough to kill cancer cells?
Nanotextures on nanoparticles and implants to kill cancer cells in a more targeted manner may just be the key to tackling resistance to traditional cancer drugs.
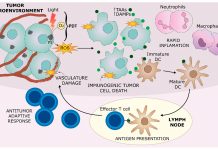
Photodynamic therapy and immune response in solid tumours
Photodynamic therapy can stimulate a person’s own immune system to better recognise – and fight – cancer tumours, say Mary Potasek, PhD and Karl Beeson, PhD of Simphotek and Theresa M Busch, PhD of the Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Pennsylvania.