Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home 2025
Archives
Training your genome
Founder and President of InsideOutBio, Alan Herbert, explores the evolving understanding of genome information storage, and the significance of repetitive sequences called flipons in genome training. These flipons can alter their shape without breaking DNA and are vital in cell biology, especially in responding to environmental stress.
An ancient therapy modernized for Clostridioides Difficile therapy
Clostridioides difficile is a type of bacteria that often affects people who have been taking antibiotics. Glenn S. Tillotson of GST Micro LLC explains how live biotherapeutic products have shown promise as a safe and effective treatment to help restore the normal gut microbiome.
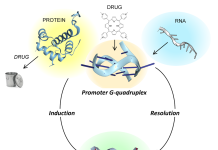
Targeting the most complex flipon of them all in the fight against cancers
In this article, Alan Herbert, the Founder, and President of InsideOutBio, guides us through targeting the most complex flipon of them all in the fight against cancers.
Ciliary biomarkers for vascular health
Ramani Ramchandran, Professor at the Medical College of Wisconsin, investigates ciliary biomarkers for diagnosing and prognosing vascular health.
Cellular scaffolding: Crowdsourcing cellular responses in health and disease
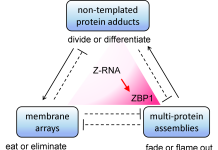
In this article, Dr Alan Herbert discusses how different types of cellular scaffolds interact and impact the risk of diseases, citing the example of Z-RNAs pushing cells to inflammatory states in tumors and autoimmune conditions, setting the stage for new therapeutics.
A century of NAD+ insights drives aging science and solutions innovations
Dr. Rebecca Crews from Renue By Science, LLC, outlines a century of NAD+ insights driving aging science and, innovative solutions and much more.
Protecting the human epigenome with nutritional epigenetics intervention programs
Dr Renee J. Dufault, Executive Director at the Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, explains the significance of nutritional epigenetics in understanding the impact of nutrients and dietary chemicals on gene expression patterns, as well as their role in the development of conditions such as autism and ADHD.
Healthy aging: A novel therapy to reverse age-related damage
What if we could turn back the clock on age-associated dysfunctions by using a therapy that not only treats symptoms but acts to correct the underlying pathology and restores cells to normal function? Lori A. Birder and Edwin K. Jackson from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, explain how this could be a possibility.
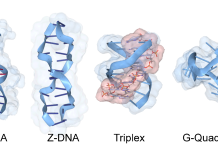
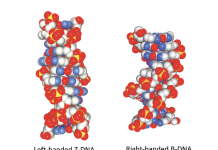
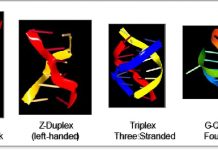
Flipons: The discovery of Z-DNA and soft-wired genomes
Alan Herbert, Founder and President of InsideOutBio, discusses alternative DNA conformations and understanding of their biological functions.
How the dark genome enlightens the molecular mechanisms of diseases
In this article, Antoinette van Ouwerkerk and Salvatore Spicuglia from INSERM highlight the significance of regulatory variants within the non-coding genome – often referred to as the ‘dark genome’ – in influencing gene expression and disease.
The role of stem cell-derived tissues in novel treatments for cardiac ailments
Curbs on animal testing mean human tissues derived from induced pluripotent stem cells offer a promising platform in discovering novel treatments for cardiac ailments.
The ethical and legal challenges of cell donation for brain organoid research
Ethical and legal concerns raised by the use of human biological materials, especially cells from adult donors and foetal tissues, must be thoroughly examined.
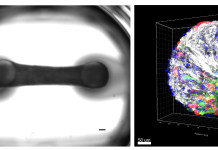
What imaging reveals about engineered endosymbionts
Ashley V. Makela and Christopher H. Contag from the Institute for Quantitative Health Science and Engineering, walk us through watching living therapeutics in action, including what imaging reveals about engineered endosymbionts.
The different facets of biodiversity
Professor F. Guillaume Blanchet from Université de Sherbrooke explores the various aspects of biodiversity and the challenge involved in monitoring it.
Arc: A new target for treating alzheimer’s disease
Antonius M. VanDongen, Associate Professor from Duke University, walks us through Arc, a new target for treating Alzheimer’s disease.
RNA and DNA flipons in health and disease
Flipons are the next step in DNA research. What they are, their role in DNA and RNA coding, their impact on medical science, and their relation to the immune system are discussed here.
Understanding thermolabile protecting groups for nucleic acid-based drugs
Serge L. Beaucage investigates thermolabile protecting groups for the amine functions of purine and pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides for the development and implementation of synthetic DNA sequences as nucleic acid-based drugs.
The idea of self-organisation in biology and its critics
Using the example of Alan Turing’s paper on morphogenesis, Ute Deichmann at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev explores self-organisation in biology.
Shrouded in genomic heterochromatin are ancient viral-like elements that could jump
Host defences operate to prevent ‘ancient viruses’ from ever jumping but, in cancers, cells lose multiple layers of ‘epigenetic’ control, and this can lead to the awakening of jumping or ‘retrotransposition’ of ancient viruses.
Information overload and the ossification of immunological research
Peter Bretscher, Faculty in the Department of Biochemistry, Microbiology and Immunology at the University of Saskatchewan questions whether there is a way of fostering resilience in immunological research.