Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home 2026
Archives
Start clean: Canada’s grapevine clean plant program
Debra Inglis and Sudarsana Poojari provide an update on Canada’s grapevine clean plant program, run in partnership with Brock University’s Cool Climate Oenology and Viticulture Institute, industry’s Canadian Grapevine Certification Network, with support from the Canadian Food Inspection Agency.
Magnetobiology: Beyond attraction
Jinxing Li and Christopher H. Contag delve into the emerging field of magnetobiology, which utilizes magnetic fields to manipulate and control living systems, while reflecting on its potential to surpass the limitations of other modalities.
Berry and honey production in Alberta: Exploring the market system
Aleksandra Tymczak studies the berry and honey industries in Alberta’s agricultural system. Here, she discusses the challenges and opportunities for farmers to access markets, as well as the current capacity for the distribution system across Alberta’s agricultural system.
Care research: The importance of philanthropy
In this exclusive interview, Dr Benson from the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center explores the importance of philanthropy and the power it has to drive innovation and collaboration, particularly in cancer research and patient care.
Reimagining mining for a net-zero future
Carbon-negative mining offers a promising path to meeting the mineral demands of the energy transition while shrinking the industry’s carbon footprint. In this article, Dr Estibalitz (Esti) Ukar examines how innovative geochemical and geomechanical processes could turn mining into a net-negative carbon industry.
Precycling: Waste to plastics resource pathways
The PRecycling project aims to recover high-quality polymeric materials from underutilized plastic waste streams, focusing on developing near-production-scale recycling processes to transform plastic waste into secondary raw materials, and enabling up to 100% recycled content incorporation in new products.
Beyond microbial fermentation: Reimagining biomanufacturing for low-resource environments
Although traditional biomanufacturing is based on microbial or mammalian cell culture, plants can be grown in bioreactors and hold enormous promise for use in resource-limited environments.
Gallium oxide: The race to power the next-generation grid and EV infrastructure
In an exclusive OAG Q&A interview, Professor Singisetti from the Department of Electrical Engineering at the University at Buffalo discusses the commercialisation path for Gallium Oxide in high-power electronics.
Lithium supplements to prevent Alzheimer’s disease: A poisoned chalice?
Matthew J. Armstrong, Anthony E. Valenzuela, and Pamela J. Lein explore the use of lithium supplements to prevent Alzheimer’s disease and whether this approach is a poisoned chalice.
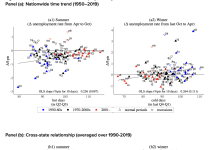
Global warming fuels unemployment rate in summer
Masahiro Yoshida from Waseda University’s Department of Political Science and Economics finds that global warming raises summertime unemployment.
Learning with AI: Losing critical thinking at the worst time
Nancy Butler Songer argues that learning with artificial intelligence is contributing to the erosion of critical thinking skills at a time when it is most needed.
How academic-tribal teams cut cancer risks in Native American communities
Learn how the Native American Center for Cancer Health Excellence addresses cancer health disparities through bidirectional research that honors tribal sovereignty.
Dynamic feedback modeling to predict random infection outcomes
Brian P. Lazzaro from Cornell University discusses the role of dynamic feedbacks in determining infection outcomes.
Safe and effective use of opioids for co-occurring disorders
Co-occurring disorders and clinical care for complex illnesses- safe and effective use of opioids may be only one of the areas where we need collaboration. Norm Buckley from the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Pain Research & Care explains.
Volunteering in rural and urban communities isn’t one-size-fits-all
Rebecca Nesbit and Laurie E. Paarlberg argue that volunteering cannot be a one-size-fits-all solution, as the experiences of rural and urban communities demonstrate.
Novel adjunct treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder: Neurofeedback and deep brain reorienting
Dr. Ruth Lanius, Scientist at London Health Sciences Centre Research Institute (LHSCRI) and Psychiatrist at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) discusses the need for novel adjunct treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), highlighting two promising approaches: neurofeedback and Deep Brain Reorienting (DBR).
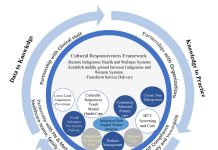
Indigenous health research program: Offering insights for better health
Dr. Mamata Pandey, Research Scientist at the Saskatchewan Health Authority in Canada shares insights from her Indigenous-partnered health research program, enhancing health.
Wellbalance elevates coaching through the science of personalized wellbeing
WellBalance’s “Wellbeing Balance and Lived-Experiences Model of Positive Wellbeing”, developed by Harvard-trained scientist Troy W. Norris, is the first scientifically validated experiential model of wellbeing.
Business education at the crossroads: Transform or face irrelevance
The article, authored by Jean Garner Stead, calls for an urgent re-evaluation of business education to foster leaders capable of creating sustainable value in a rapidly changing world.
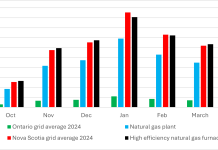
Cold climate heat pumps for GHG emission reductions: A smart-grid approach
Dr. M.F. Lightstone, P.Eng., FCSME, FCAE, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at McMaster University, presents a smart-grid approach for cold climate heat pumps aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.