Home 2024
Archives
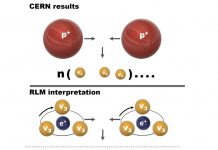
Neutrino production in proton-proton collisions supports the rotating lepton model
Direct observation of neutrino production in proton-proton (pp) collisions at CERN LHC lend strong support to the Rotating Lepton Model, Constantinos G. Vayenas(1), Dionysios Tsousis(1,2) and Eftyhia Martino1 ((1)University of Patras, (2)Stanford University) tell us.
Microfluidic microbial bioreactors: How studying microbes at the microscale can help empower microbiology
Long before the existence of microbes was known, humans were unknowingly harnessing their power through practices such as brewing, bread leavening, or cheesemaking. These processes extended the shelf life of food, enhanced its nutritional value, and significantly contributed to the advancement of industry and civilization.
tRNA: The operational RNA code and protein folding
Charles W. Carter, Jr., from the Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, relates molecular recognition used in genetic coding to structures of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and their cognate tRNAs.
Digital Life Norway (DLN) Initiative to foster and boost transdisciplinary biotechnology research and innovation
Meeting the rapid developments in biotechnology by fostering transdisciplinarity, including digitalisation and big data, to create convergence for innovation in a virtual centre.
Opinion: Do universities help or hurt innovation?
Do Universities help or hurt innovation? Find out in this 25-year academic entrepreneur’s anecdotal perspective of starting companies and developing implants. Thomas J. Webster shares his opinion here.
Microbe development for the biomanufacturing age
Joe Price, Dr Kang Lan Tee & Prof Tuck Seng Wong, explore adopting a holistic approach to microbe development for the age of biomanufacturing.
Responsible and ethical conduct of research: Principles to uphold
Greg M. Swain, Professor of Chemistry at Michigan State University, emphasizes the importance of responsible and ethical conduct of research (RECR) in scientific progress.
Superconductivity and related macroscopic quantum phenomena
John H. Miller, Jr., from the University of Houston, Dept. of Physics and Texas Center for Superconductivity, walks us through superconductivity and related macroscopic quantum phenomena.
Purple non-sulfur bacteria and the circular economy
Arpita Bose, Associate Professor at Washington University in St. Louis, discusses the potential of microbial solutions in supporting sustainable and environmentally responsible alternatives to the traditional linear economy.
Drug repositioning using multiple gene expression profiles
Chuo University’s Professor Y-h. Taguchi places focus on drug repositioning using multiple gene expression profiles
Using lotteries instead of auctioning is both inefficient and inequality-creating
Yew-Kwang Ng, Emeritus Professor in the Department of Economics at Monash University, compares the use of the lottery and auctioning to allocate scarce goods.
Towards generalised pairs trading strategies through AI
Here, we learn about Professor Chien-Feng Huang’s interdisciplinary research at the National University of Kaohsiung in Taiwan, concerning the move towards generalised pairs trading strategies through artificial intelligence.
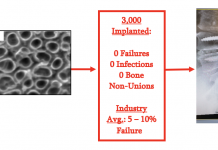
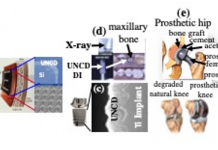
Ultrananocrystalline diamond (UNCD™) coating for new-generation implantable medical devices/prostheses
In this materials science piece, Orlando Auciello, describes the development of a unique multifunctional/best biocompatible ultrananocrystalline diamond (UNCDTM) coating for new-generation implantable medical devices and prostheses.
What remains when two neutron stars collide?
Distinguished Professor Susan M. Scott and Dr Karl Wette from the Australian National University examine what remains when two neutron stars collide in this exciting gravitational astrophysics focus.
AI and modern experimental biology: A historical perspective
Ute Deichmann, Director of the Jacques Loeb Centre for the History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, discusses the adoption and limitations of Artificial Intelligence within modern experimental biology.
Understanding T lymphocytes inner workings to harness therapeutic potential
Leslie J. Berg, PhD from the University of Colorado, Anschutz School of Medicine, sheds light on understanding the inner workings of T lymphocytes to harness their therapeutic potential.
Data management plans as a tool for making data fair
Andy Götz (ESRF Data Manager and PaNOSC Coordinator), explores if and how Data Management Plans (DMPs) are essential for making data FAIR.
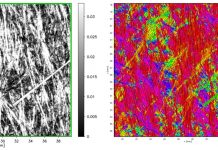
Quality control for the recycling of carbon fibre
Due to the inevitable variability of the end-of-life input material, the resulting recycled fibre and nonwoven or woven material will have a higher degree of variability than virgin material. To make sure such recycled fabric is usable for high-quality applications, additional methods for quality control are required.
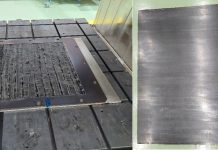
Recycling fibre-reinforced composite parts
Uncured carbon fibre recycling by Bulk Moulding Compound (BMC).
Fresh prepreg multilayer scrap reuse
To address waste generated during production, a processing route for uncurde material is developed in MC4. Multilayer fresh prepreg scrap is processed to obtain new intermediate products that can be used to manufacture new parts.