Oils by Simpson of 2012 supplies organic full-spectrum CBD cannabis oil products. CBD oil is popular and commonly used for its potent therapeutic benefits, but what about its effect on pain? Here’s what the research shows
CBD oil is a popular natural treatment for various physical and mental health conditions. CBD, short for cannabidiol, is a natural cannabinoid compound found in the cannabis plant. Cannabinoids like CBD can be extracted from the plant and used in various cannabis-based products that are available for purchase. CBD oil is CBD extract mixed with a type of carrier oil, like hemp or coconut, and can be applied topically or taken sublingually.
Pain is felt when a signal travels through nerves to the brain. The underlying cause of pain can be complex and from many different factors (1). Pain levels can vary from minimal to debilitating and can be short-term or long-lasting. Chronic pain occurs when pain is ongoing and persists for more than six months, even when the cause (illness or injury) has dissipated. Chronic pain can also have many underlying causes, although it is most commonly due to dysfunctional nerves or inflammation (2).
Pain and CBD
While studies regarding CBD oil benefits are highly limited due to restrictions on cannabis use and research that can be carried out, as the legalisation of cannabis grows, more in-depth and long-term research involving human participants is expected to happen.
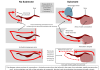
The endocannabinoid system
Most studies on pain have involved numerous cannabinoids, like THC or a combination of several, rather than just CBD alone. There are over 100 different cannabinoids in the cannabis plant, each with slightly different profiles and effects (3). Besides CBD, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a notable cannabinoid and can produce psychoactive effects experienced as a “high.” All cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a cell-signalling system present in all mammals.
The ECS is responsible for balancing and regulating body processes that control everything from our mood, sleep, immune system function and metabolism. The ECS consists of cannabinoids produced naturally, called endocannabinoids, and cannabinoid receptors spread throughout the brain and nervous system (4). Cannabinoids like CBD can interact with these receptors and activate systems that alter how the brain perceives pain.
Studies on pain and CBD oil
While CBD doesn’t create a euphoric “high” like THC, its complex effects can help the body utilise its own endocannabinoids. A 2015 study suggested that CBD, in conjunction with other cannabinoids, can influence receptor systems within our body and the ECS. CBD is shown to increase the levels of anandamide in our bodies. This compound has been associated with reducing pain perception and improving mood in individuals (5).
However, recent evidence suggests CBD doesn’t wholly reduce pain intensity, but makes the pain feel less unpleasant. A study carried out in early 2021 investigated the effects of cannabinoid drugs on pain by safely inducing experimental heat pain before measuring how the nervous system reacts and responds to it. By using pure CBD isolate oil, researchers found that while CBD didn’t reduce the volume of the pain, it made the pain less bothersome (6).
While the results of these studies and many others remain promising, more research is needed to verify the benefits of CBD oil when it comes to pain relief.
CBD oil for different types of pain
As the underlying causes and symptoms of pain are complex, individuals can experience different types of pain.
Chronic pain
Chronic pain is classified as high levels of pain that last longer than a couple of months and don’t go away even after recovering from an injury or illness. Examples of chronic pain include back pain and frequent headaches. While patients can manage chronic pain with several treatment options like acupuncture, medication and surgery (7), severe types of chronic pain generally cannot be cured and are monitored and maintained throughout the individual’s life.
Because of the long-term nature of chronic pain, some patients are beginning to seek natural and alternative treatment methods to traditional medication, which are often associated with adverse side effects. CBD oil remains a popular choice as studies have been favourable regarding the effects of CBD and how it can reduce the severity of chronic pain output.
“Pain is felt when a signal travels through nerves to the brain. The underlying cause of pain can be complex and from many different factors. Pain levels can vary from minimal to debilitating and can be short-term or long-lasting.”
A 2017 report summarised the key findings from various studies and investigated CBD use for general chronic pain. After compiling the results of dozens of trials and reviews, researchers concluded that substantial evidence suggested that cannabis could be a viable treatment option for adults experiencing chronic pain (8). Another study supported these findings, with researchers noting that cannabinoids like CBD could offer a new treatment option for chronic pain patients by reducing pain and inflammation. They also found patients were unlikely to build up a tolerance to the effects of CBD, meaning the dosage did not need to be increased over time (9).
Neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain is caused by nerve irritation due to damage. It is often described as causing shooting or burning sensations, with affected areas being extremely sensitive when touched. Neuropathic pain affects the somatosensory nervous system, so symptoms of this type of pain include pins and needles, excruciating pain levels, and difficulty detecting numbness or changes in temperature (10).
The causes and treatment available for neuropathic pain vary case-by-case. Some factors that trigger neuropathic pain include alcoholism, exposure to toxins and nutritional imbalances. Treatment can also vary depending on the severity of the pain. Generally, antidepressants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help ease the patient’s pain (11). However, many people will require more potent painkillers and will combine natural sources of pain management, like CBD oil, with their traditional medication.
Research regarding CBD and neuropathic pain are mixed. A 2017 review looked at different trials with over 1,000 participants that compared selected cannabinoids in their treatment of neuropathic pain. Researchers found CBD could help with chronic neuropathy pain in humans (12). However, researchers in a 2018 review concluded that while cannabis-based medicine shows promise, this may be outweighed by its potential harms. The review looked at over 16 studies that analysed the effects of cannabis-derived medications, including CBD-based products (13). This suggests more research is needed to understand the role CBD can play in neuropathic pain symptom relief and treatment.
Cancer treatment pain
One of the most challenging stages for individuals with cancer is dealing with the numerous side effects of the disease treatments. Cancer treatment options vary, but common ones include hormone therapy, immunotherapy and chemotherapy. These treatments can result in a range of side effects, including pain, vomiting, nausea and lack of appetite (14).
The cancer patient often experiences chronic and persistent pain. The research on CBD oil and oral sprays and their effects on cancer pain management has been promising. Researchers have investigated CBD oil and its role in reducing inflammation and overall discomfort due to health conditions like cancer.
A 2013 study involving advanced cancer patients with cancer-related pain looked at how THC-CBD extract, in conjunction with opioids, produced more effective pain relief than opioids alone (15). Another 2018 review, which looked at studies conducted from 1975 to 2018, assessed the effects of CBD in relieving chronic pain. A range of pain conditions was examined, including cancer and neuropathic pain. Researchers concluded that CBD was effective in overall pain management across different pain types with minimal side effects experienced (16).
CBD oil and inflammation
Pain and inflammation walk hand-in-hand. Elevated inflammation levels cause inflammatory pain due to an inappropriate immune system response, which is associated with conditions like arthritis (17). CBD has shown promise in reducing inflammation in the body, particularly the nervous system and brain. This may benefit individuals who experience chronic pain and have trouble sleeping, resulting in insomnia and specific immune system responses.
Inflammation can be chronic or acute. Acute inflammation generally follows an illness or infection and results in redness and swelling to the affected area. Chronic inflammation is the result of a prolonged inflammatory response. The increased oxidative stress can be detrimental to organs and tissues (18).
“Chronic pain occurs when pain is ongoing and persists for more than six months, even when the cause (illness or injury) has dissipated. Chronic pain can also have many underlying causes, although it is most commonly due to dysfunctional nerves or inflammation.”
Studies investigating the relationship between CBD and arthritis have mainly been carried out with animals. A 2016 study investigated the effects of CBD on rats with arthritis. Researchers noted a significant reduction in signs of pain and inflammation with reduced swelling without adverse side effects (19). While the anti-inflammatory effects of CBD can prove beneficial to patients with arthritis, more studies involving humans are needed.
The side effects of pain
Pain is complex and caused by different factors that often compound to transmit information to the brain. In many cases, pain is caused by a specific injury or health condition, but in others, the underlying reasons can be less obvious or entirely unknown, requiring numerous tests (20). Whatever the cause, pain can be highly debilitating and create additional ailments or side effects that are often overlooked.
Common side effects associated with pain include:
- Decreased mood.
- Changes in appetite.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Decreased sleep quality.
Our physical and mental health is intrinsically linked. Individuals with high levels of pain are more likely to develop depression and anxiety. Chronic pain can also result in reduced sleep quality or even insomnia as the intensity of the pain prevents the patient from having a restful sleep (21). All of these side effects can spiral and create a feedback loop that worsens the level of pain.
Anxiety and depression
CBD has shown promise in improving mood and promoting the levels of “happy hormones” within the body. Researchers believe that this effect is triggered by CBD’s positive impact on serotonin receptors in the brain and its response to serotonin. While various factors can cause depression, low serotonin levels are strongly linked to mood, anxiety and depression (22).
A 2018 review looked at existing studies and concluded that CBD has anti-anxiety and antidepressant effects, which may improve mood when stress is experienced (23).
Sleep quality
CBD may be able to help improve the quality of sleep in patients with elevated levels of pain. A 2012 study investigated CBD dosage and sleep duration and found individuals who received 160 milligrams of CBD were able to sleep longer than those who were given a placebo (24). The reason behind this can be due to the interaction between CBD and the ECS, which promotes anti-anxiety effects. However, researchers have also linked CBD intake to reduced cortisol release.
Individuals with insomnia are known to have elevated cortisol levels, also known as the stress hormone, at night, preventing them from falling and staying asleep. Researchers in a 2019 study found cortisol levels decreased significantly when taking CBD oil, suggesting CBD affects the release of cortisol and can be taken as a potential sedative (25).
The bottom line
While there isn’t conclusive evidence to support CBD and CBD oil as a preferred pain management option for patients with high pain levels, researchers conclude that CBD has much potential.
CBD is well-tolerated; however, individuals should always discuss CBD with a health professional before using it for the first time.
1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6676152/
2 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4530716/
3 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3736954/
4 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4789136/
5 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4604191/
6 https://psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037%2Fpha0000465
7 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5771233/
8 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK425767/
9 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3371734/
10 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5371025/
11 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2844009/
12 https://journals.lww.com/anesthesia-analgesia/Fulltext/2017/
11000/Selective_Cannabinoids_for_Chronic_Neuropathic.32.aspx
13 https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD012182.pub2/full
14 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6123577/
15 https://www.jpsmjournal.com/article/S0885-3924(12)00439-3/fulltext
16 https://www.jpsmjournal.com/article/S0885-3924(12)00439-3/fulltext
17 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5805548/
18 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7147972/
19 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4851925/
20 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5573040/
21 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4046588/
22 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4471964/
23 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6161644/
24 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24281562/
25 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6326553/pdf/18-041.pdf
Please note: This is a commercial profile
© 2019. This work is licensed under CC-BY-NC-ND.