Heiko Rischer, Research Team Leader, VTT, argues here that lab-grown coffee and cellular agriculture represent the next food revolution
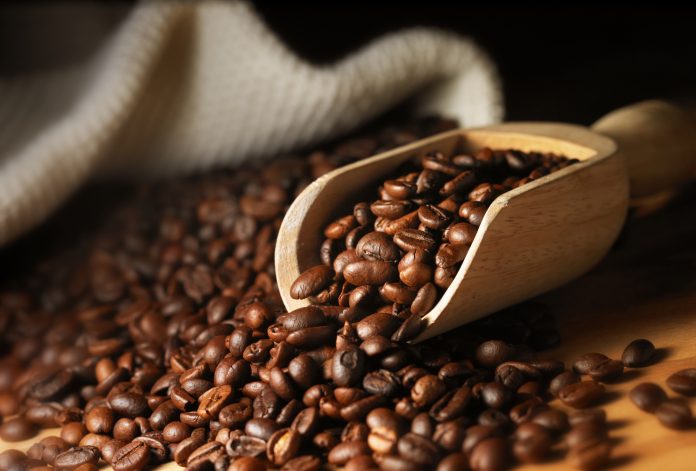
A tasty cup of coffee through cellular agriculture? Yes, please. VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland has successfully produced coffee cells in a bioreactor. This achievement is an example of how cellular agriculture can show us the way towards sustainable food production.
Our current way to produce food is unsustainable and unethical. Take coffee, for example, the demand keeps on rising, but suitable areas for coffee plantations are shrinking due to climate change. More acreage is used to meet the demand, which leads to deforestation – particularly in sensitive rainforest areas.
VTT’s scientists decided to tackle this challenge by producing coffee through plant cells in their laboratory. The research work started by initiating coffee cell cultures, establishing respective cell lines and transferring them to bioreactors to produce biomass. After analysing the biomass and developing a roasting process, the first coffee samples were brewed. According to VTT’s trained sensory panel and analytical examination, they smell and taste similar to conventional coffee.
The process required input from several disciplines such as plant biotechnology, chemistry and food science. The procedure is based on existing technology, but needs to be scaled and optimised for commercial production. The next steps include regulatory approval and introduction to the market. According to VTT’s estimates, this could all be accomplished within a few years.

Food system must change radically
Our entire food system is facing similar sustainability challenges as coffee production. There are major concerns related to hunger, health and the environment.
It’s estimated that we need 60% more food in 2050 for our growing global population. However, we only have 2% more land available for agriculture. Currently, more than 820 million people have insufficient food, and malnutrition complicates the situation further. We need to produce more food, but not just generate calories, the food must be safe, healthy and nutritious.
Furthermore, food production causes major environmental issues. It is accountable for up to 25% of greenhouse gas emissions and 75% of freshwater consumption. The production of many everyday food items causes deforestation. Pollution, erosion, and insect extinction are other examples of environmental damage.
Smarter primary production may increase the efficiency of conventional agriculture and bring some relief, but that’s certainly not enough. It’s time to upgrade the whole system.
Cellular agriculture: a sustainable alternative
Cellular agriculture has the potential to disrupt our current food production. It allows us to produce plants and animal-based food ingredients by microbial and plant cells, providing an alternative to unsustainable and unethical production methods.
Cellular agriculture uses cells as factories. These cells – microbes, animal or plant cells – are cultivated in bioreactors to produce ingredients that are traditionally grown on fields or animal husbandries. Through cellular agriculture, we can grow plants materials anywhere: in cities, deserts or even in space. Pesticides or other harmful chemicals are not needed because the conditions are fully controlled and sterile.
Cell-based plant ingredients can be added to existing food products or used to create completely new ones. The biomass can contain a high protein content, dietary lipids or other health-promoting components to tackle malnutrition. All lab-grown products must also pass strict safety tests that ensure their quality.
Growing plant cells in bioreactors instead of cultivating them in fields reduces land use and decreases greenhouse gases. Locally produced food requires less transportation, thus reducing air pollution. Even food waste is cut down: with cellular agriculture seeds and peels are simply not produced.
High demand sets ground for new business
The expected demand for new products based on cellular agriculture is extremely high. This generates new business opportunities. Next, we need companies that are willing to explore these opportunities in their product development and create new commercial applications.
Many companies have already started this journey. First consumer products have been launched, and a growing number of projects are going on around the world. Quorn has been one of the pioneers: their story started already in the 1960s and today there are millions of people eating Quorn meals. Solar Foods from Finland is another example. It has invented a way to produce natural protein from carbon dioxide using electricity. The company aims to start commercial production by the end of 2022.
VTT is a visionary forerunner in the field of cellular agriculture with a track record of innovations that pioneer the future. Besides lab-grown coffee, we have developed a method for producing egg white without chicken, for example. Producing egg white protein by cellular agriculture generates about 75% fewer greenhouse gases and uses 90% less land when compared to chicken farming. Our award-winning process is safe, cost-effective and scalable.

Seize the opportunities in cellular agriculture with VTT
VTT collaborates with large enterprises and small companies to boost their development based on cellular agriculture. VTT CellularFood programme helps these companies to develop their new processes and products step by step. In addition to technology development, the process includes risk and cost assessment, and it helps to make informed decisions based on pilot findings.
VTT’s scientists can help you to identify the potential that cellular agriculture offers for your business and assist in the development of your own product – from analysis to piloting. We offer a unique combination of cross-disciplinary expertise, facilities and infrastructure. Ultimately, all efforts should result in more sustainable and ethical production of healthy food for the benefit of the consumer and the planet.
*This is a commercial profile.
© 2019. This work is licensed under CC-BY-NC-ND.