Eric Buckland of Translational Imaging Innovations looks at ophthalmic drug development and how better clinical endpoints can improve success rates
Late-stage failure rates drive the cost of ophthalmic drug development
A 2016 study analyzed the costs of drug development from discovery through regulatory approval. When accounting for the failure rates and the cost of capital, the total cost to bring a new drug to market (2103 dollars) is $2.5B over 10.9 years. The primary factor is the low program survival rates at critical phases in the drug development pipeline. 60% of drug candidates survive Phase I clinical trials and only 36% of candidates survive Phase II trials, the first tests of safety and effectiveness, respectively.
Only 56% of Phase II survivors then make it to the clinic. This study was not specific to ophthalmology, but ophthalmology is the most expensive therapeutic area for clinical trials after pain management. Clearly there is a need for better early tests of drug efficacy, as well as better ways to identify patients as appropriate candidates for emerging therapies.
Better clinical endpoints and biomarkers are essential to reducing late-stage failures
Two recent conferences held in Boston explored the challenges of developing therapeutic solutions for degenerative eye diseases that impact more than 200 million people world-wide.
A common theme in these two conferences was the critical role that disease biomarkers and clinical endpoints play throughout the drug development process. Biomarkers validated as surrogates for clinical outcomes are essential to the design of efficient clinical trials, particularly for slowly progressing diseases. Biomarkers and clinical endpoints that improve phase-to-phase success rates reduce the costs of clinical trials, accelerate time to market, and almost certainly support better patient outcomes.
Biomarker discovery is driven by imaging and functional vision tests
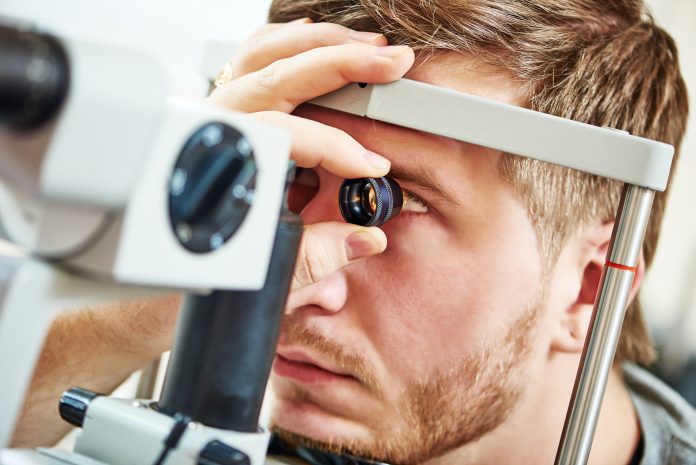
Ophthalmology benefits from an exquisite array of imaging technologies and functional vision tests. Because the eye is transparent, imaging modalities such as optical coherence tomography and fundus photography provide three dimensional and wide field images of the retina. Adaptive-optic enhanced imaging systems provide cellular-level visualization of photoreceptor involvement in degenerative eye disease. The ophthalmic research community has developed a rich understanding of the retinal structural and functional anatomy elucidated by modern imaging techniques. Much work remains to discover imaging biomarkers that provide solid prognostic evidence for a patient’s risk of accelerated disease progression and to validate imaging biomarkers as clinical trial endpoints.
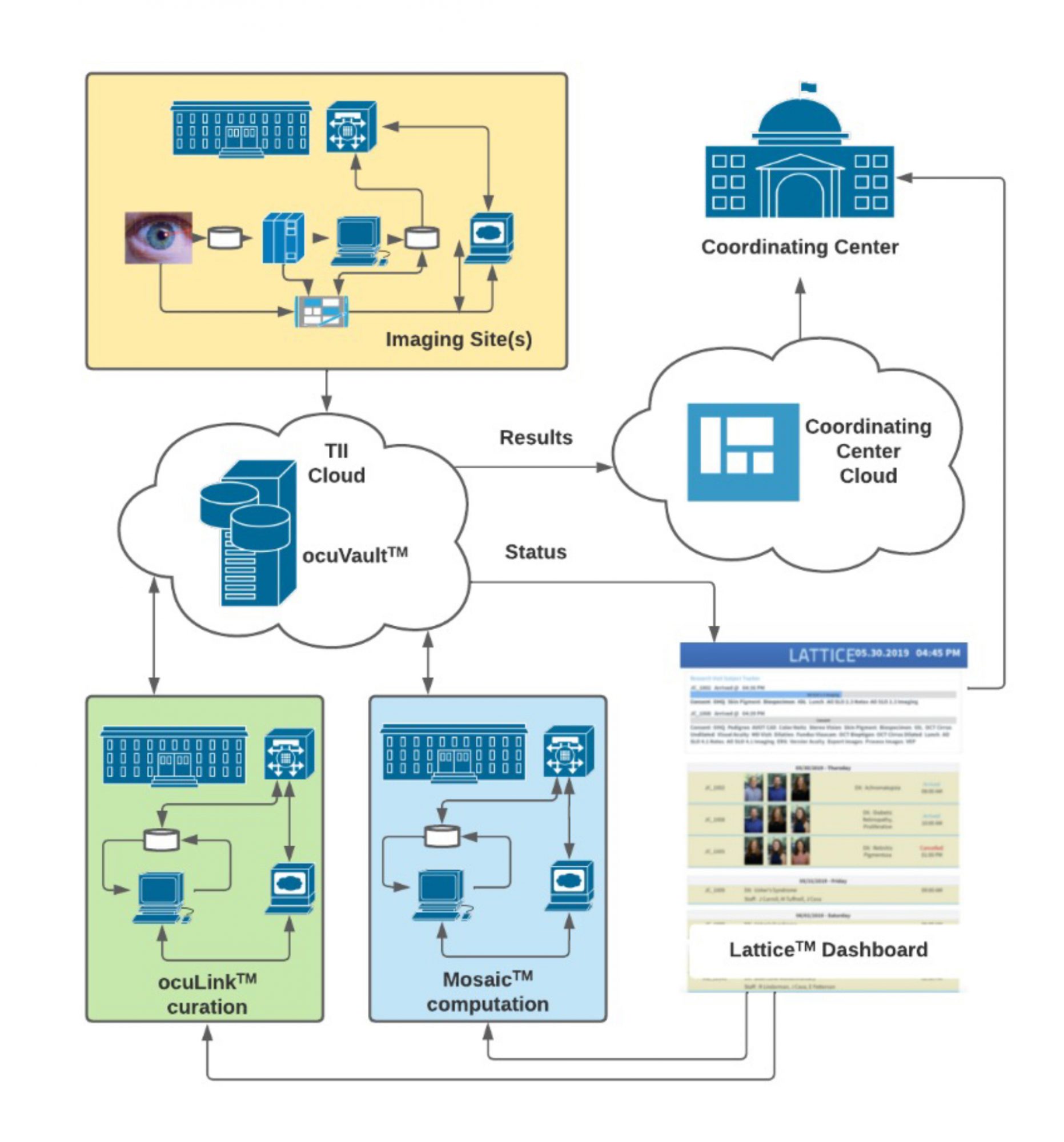
Translational Imaging Innovations is deploying end-to-end data solutions for ophthalmic research and clinical trials
The TII-designed Integrated Translational ImagingTM platform reduces the burden of harnessing images and data throughout the clinical development process Our strategy is based on the principles of FAIR Data Access, Security, and Traceability:
FAIR: Images and Data must be Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable. The TII Data GenomeTM is our ontology for a scalable, extensible, and FAIR data infrastructure. The TII Data Genome is reflected in ocuVaultTM, a database that provides accessibility to data within and across projects. ocuVaultTM is suitable for single investigator projects and for larger multi-investigator, multi-site programs. ocuVaultTM is DICOM compatible and addresses a key gap in ophthalmic imaging interoperability.
Security: Protection of patient health information (PHI) in research and clinical trials is critical. ocuVaultTM automatically segregates PHI from images and observational data, simplifying the control protected information while reducing friction in data analysis workflow.
Traceability: ocuVaultTM ensure full traceability of source data, metadata, and analyses. Every patient, study, experiment, test, and image is coded with a unique identifier that travels with each data object. This identifier supports complete upstream and downstream traceability, simplifying data validation and data audits, and reducing errors associated with manual transcription and file naming.
TII Applications are designed to meet the challenges of developing and validating biomarkers and clinical endpoints
The TII Application Layer provides useful workflows for curating and analyzing images and data, uniformly reading and writing to ocuVaultTM. ocuLinkTM is a vendor neutral, multimodal image curation, visualization, and annotation application. ocuLinkTM includes an easy-to-use, feature-rich collection manager and annotation engine that serves both as an image grading portal and a labeling environment for training, testing, and validating machine learning algorithms. MosaicTM is our computational engine. MosaicTM supports batch processing of images through customizable recipes of sequential algorithms. Mosaic automates processes from image segmentation through quantitative analysis. Mosaic supports parallel processing of multiple recipes for efficiently challenge-testing algorithms.
ocuVaultTM and ocuLinkTM are implemented today in laboratory research automation and cloud-based image processing applications
ocuLinkTM is now deployed to automate the transfer of images from imaging devices to ocuVaultTM, eliminating time consuming and error prone manual image organization steps for our customers. The TII team is currently integrating application-specific process automations, shaving hours, days or even weeks from data management and analysis tasks.
Whatever the implementation, Translational Imaging Innovations is committed to delivering the most convenient and productive solutions for ophthalmic biomarker discovery and clinical endpoint validation. TII’s goal is to enable translational researchers to develop better diagnostics and better therapies, with more predictable benefits – faster, at a lower cost, and with less frustration.
1. DiMasi JA, Grabowski HG, Hansen RW. Innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: New estimates of R&D costs. J Health Econ. 2016 May;47:20-33.
2. https://aspe.hhs.gov/reports/examination-clinical-trial-costs-barriers-drug-development-0
3. 3rd Gene Therapy for Ophthalmic Disorders | September 2022 | Boston (genetherapy-ophthalmology.com)
4. Dry AMD Therapeutics Summit | November 30 – December 2, 2022 (dry-amd-therapeutics.com)
5. FDA approves novel gene therapy to treat patients with a rare form of inherited vision loss | FDA

This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International.