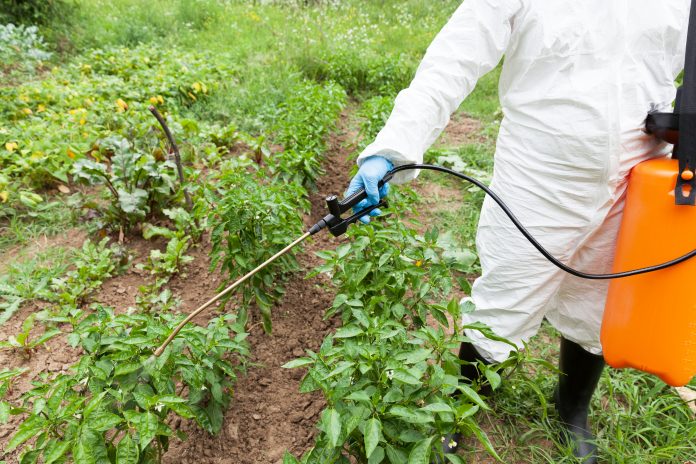
Cecilia Van Cauwenberghe from Frost & Sullivan’s TechVision Group charts the influence of synthetic pesticides on human health and the global ecosystem
Synthetic pesticides constitute chemicals that are used for the control and management of plant pests such as weeds, insects, and/or fungal pathogens. Synthetic pesticides can be classified into four main categories according to their chemical composition: Organochloride, organic phosphorus, carbamate, pyrethrin and pyrethroid. Playing a fundamental role in crop safety and productivity enhancement, synthetic pesticides have dominated the global market during the past decades. However, the rising concerns about the negative impact of the use of crop protection chemicals on health have led to a greater interest in sustainable agricultural practices across the world (Dey, 2019), as well as, the implementation of integrated pest management (IPM) systems and organic farming practices. Governments worldwide have stringed regulatory aspects associated with the manufacture, distribution, and use of harmful chemical pesticides. In parallel, synthetic pesticides are designed to increase their efficacy but conferring minimal damage to human health and the global environment.
Direct and indirect exposure to pesticides
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 1,000,000 people are affected by acute poisoning by contact with the pesticide. Pesticides can affect the health system either directly through active ingredients in the pesticide formulation, or indirectly through contaminants that occur as impurities inside the active ingredient. Moreover, compounds can be degraded as a result of microbial, or chemical and photochemical action, hence generating new constitutes. Additives in the form of preservatives, emulsifier’s wetting agents, solvents or diluents, adhesives and buffers can interact with active ingredients.
A summary of the epidemiological literature published between May 2018 and May 2019 examines in detail the association between exposure to synthetic pesticides and human health, starting with agricultural workers (Curl et al., 2020). According to this analysis, exposure to synthetic pesticides is associated with adverse health outcomes in agricultural workers. The authors describe these outcomes highly related to different types of cancers, genomic damage, oxidative stress, neurological disorders and respiratory, metabolic and thyroid effects.
Beyond direct exposure, pesticides in water resources adversely affect both human health and entire ecosystems. Recognised as potential mutagens, these chemicals are supposed to trigger deviations in the genomic expression of the DNA (Hassann and Nemr, 2020).
Synthetic pesticides: Final remarks
Essential for life, water is severely affected by the presence of synthetic pesticides. Both groundwater and surface water suffer the threat associated with the introduction of pesticides. In particular, groundwater is critical because pesticides cannot be eliminated and pollutant concentration cannot be promptly reduced.
Biomagnification and bioconcentration constitute the two principal mechanisms directly impacting health. Biomagnification governs the increasing level of a chemical for food energy that is converted within the food chain. Bioconcentration outlines the transmission of a chemical agent into an organism from the surrounding medium.
An increasing number of crop science stakeholders are driving their attention to the development of better biopesticides, significantly raising their demand. The next five years are expected to evidence a growing interest of the market participants in more sustainable solutions through the increasing use of biopesticides.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank all contributors from industry involved with the development and delivery of this article from Frost & Sullivan.
Further reading
- Curl, C.L., Spivak, M., Phinney, R. and Montrose, L., 2020. Synthetic Pesticides and Health in Vulnerable Populations: Agricultural Workers. Current Environmental Health Reports, 7(1), pp.13-29.
- Dey, M. 2019. Global Analysis of Major Crop Protection Companies. Frost & Sullivan research Service. Industry Research Analysis, 9AB8/2A, Chemicals, Materials & Foods.
- Hassaan, M.A. and El Nemr, A., 2020. Pesticides pollution: Classifications, human health impact, extraction and treatment techniques. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research.