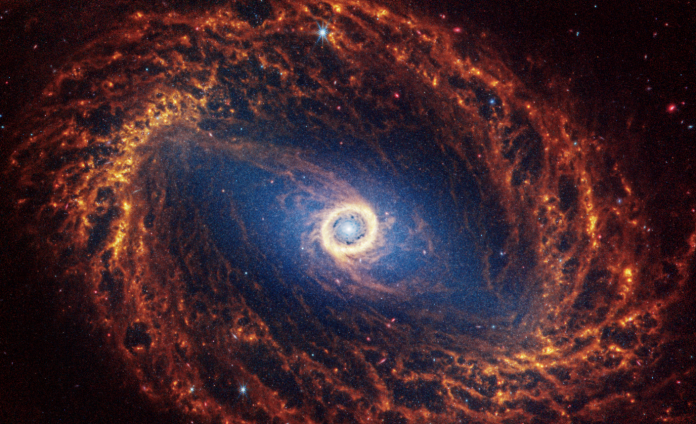
2024 was a year of remarkable achievements for NASA, marked by groundbreaking missions, scientific discoveries, technological advancements and continued space exploration. As we prepare for 2025, the agency continues to push the boundaries of human exploration and knowledge
NASA continues to push its programs deeper into space to help us further understand the universe around us. With one eye on the future of space, the agency also continues to work on the present, making significant strides in Earth science and studying our planet’s climate and environment.
Space exploration and returning to the Moon
This year (2024), NASA’s Artemis program took significant strides towards its goal of returning humans to the Moon. Key milestones included:
- Artemis II Crew Selection:
- The announcement of the crew for Artemis II, the first crewed mission to the Moon in over 50 years.
- Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS):
- The successful delivery of scientific payloads to the Moon’s surface through commercial partnerships. This innovative approach has streamlined the process of lunar exploration and opened up new opportunities for scientific discovery.
- International Collaboration:
- Strengthening international partnerships to support lunar exploration and scientific research. By working with other space agencies, such as the European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), NASA aims to maximize the benefits of lunar exploration and share the costs and risks.
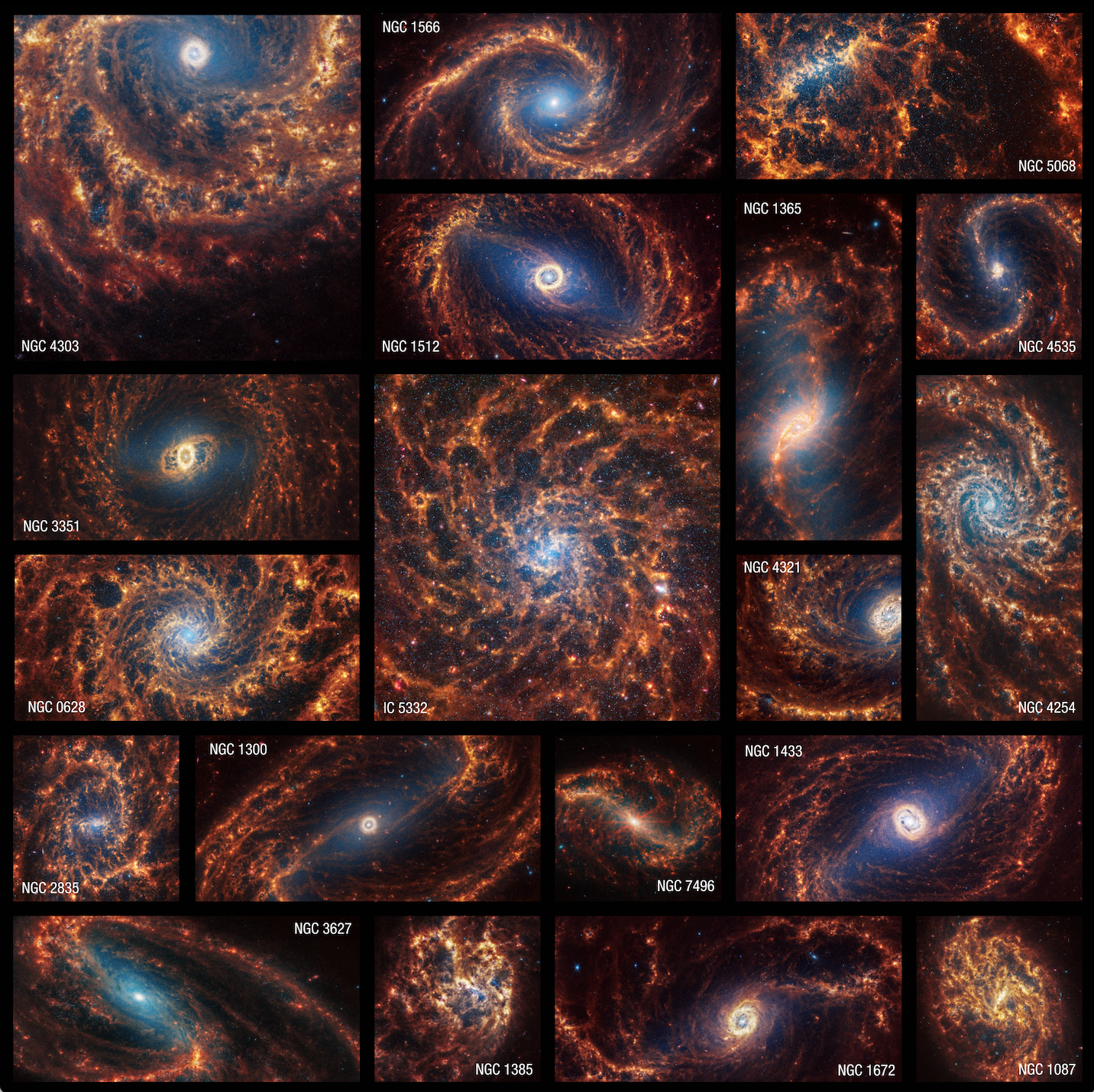

NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), PHANGS Team, Elizabeth Wheatley (STScI)
Exploring the Cosmos
NASA’s missions to explore the solar system and beyond yielded groundbreaking discoveries:
- James Webb Space Telescope (JWST):
- The telescope continues to astound scientists with its ability to peer deeper into the universe than ever before. JWST has captured stunning images of distant galaxies, exoplanets, and nebulae, providing unprecedented insights into the formation and evolution of the cosmos.
- Europa Clipper:
- Launched on a mission to Jupiter’s icy moon Europa, this spacecraft is equipped to investigate the potential for life in Europa’s subsurface ocean. By studying Europa’s surface and subsurface, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of the conditions necessary for life to exist beyond Earth.
- Voyager Mission:
- The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft, launched in 1977, continue to explore the outer reaches of our solar system. These intrepid probes have provided valuable data on the heliosphere, the region of space influenced by the Sun’s magnetic field.
- Mars Exploration:
- NASA’s Mars rovers, Perseverance and Curiosity, continue to explore the Red Planet, searching for signs of ancient life and studying Mars’ geology and climate history.
- Asteroid Sample Return Missions:
- Missions like OSIRIS-REx and Hayabusa2 have successfully collected samples from asteroids and returned them to Earth for analysis. These samples provide valuable clues about the formation of our solar system and the potential for resource extraction in space.
Earth science and climate change
NASA’s Earth science missions are vital in understanding our planet’s complex systems and addressing pressing environmental challenges. In 2024, NASA continued to push the boundaries of Earth observation and climate modelling:
- PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem):
- This advanced satellite mission is designed to study the intricate interactions between the ocean, atmosphere, and climate. By monitoring factors like plankton blooms, aerosol particles, and cloud formation, PACE provides critical data to assess the health of our planet’s ecosystems and predict future climate trends.
- TEMPO (Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution):
- TEMPO is a powerful instrument that monitors air quality with unprecedented detail. It provides hourly snapshots of air pollution levels across North America, helping to identify pollution sources, track air quality trends, and inform public health initiatives.
- Climate Modelling and Prediction:
- NASA’s climate scientists are at the forefront of developing sophisticated climate models that simulate Earth’s climate system. These models help us understand past climate changes, predict future trends, and assess the impacts of human activities on the environment. By improving the accuracy of climate models, we can make more informed decisions about mitigating climate change and adapting to its effects.
Space exploration: Human spaceflight
The International Space Station (ISS) continued to serve as a vital platform for scientific research and technological advancements in 2024:
- Crew rotations:
- Seamless crew rotations ensured a continuous human presence on the ISS, allowing for uninterrupted scientific research and technological experiments. Astronauts from various space agencies, including NASA, Roscosmos, ESA, JAXA, and CSA, worked together to conduct a wide range of experiments in microgravity.
- Commercial Crew Program:
- The successful implementation of the Commercial Crew Program allowed for increased access to the ISS, reducing costs and enabling more frequent missions. Commercial partners, such as SpaceX and Boeing, provided reliable and efficient transportation for astronauts, ensuring the continued operation of the ISS.
- Artemis Generation Astronauts:
- NASA welcomed a new class of astronauts who will play a pivotal role in future missions, including the Artemis program. These highly skilled individuals will help push the boundaries of human exploration and contribute to the advancement of space science and technology.
Aeronautics and future technologies: Shaping the future of flight
NASA’s Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate continued to innovate and develop cutting-edge technologies to revolutionise aviation:
- X-59 Quiet Supersonic Aircraft:
- NASA’s X-59 is an aircraft designed to reduce the sonic boom associated with supersonic flight. By mitigating the noise impact, this aircraft could enable faster and more efficient air travel.
- Advanced Air Mobility:
- NASA is at the forefront of developing advanced air mobility concepts, including air taxis and urban air mobility vehicles. These innovative aircraft have the potential to revolutionise transportation, reducing congestion and improving accessibility.
- Sustainable Aviation:
- NASA is committed to reducing the environmental impact of aviation. Researchers are exploring various technologies, such as electric and hybrid-electric propulsion, advanced materials, and innovative air traffic management systems, to make air travel more sustainable.
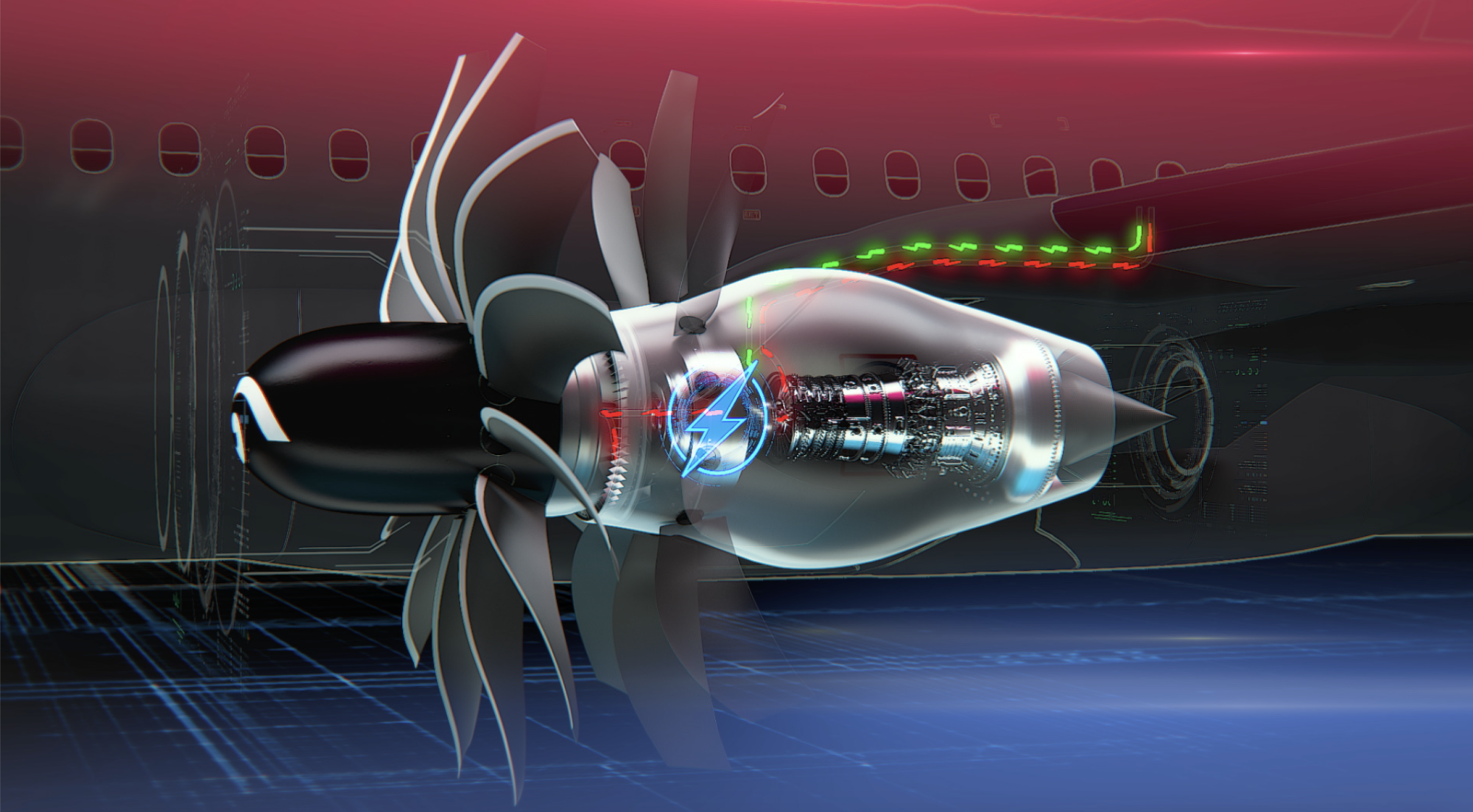
This artist concept shows a NASA-developed small-core jet engine installed in General Electric Aerospace’s CFM RISE jet engine design. The more fuel-efficient small core powers a large open turbofan, which also helps increase efficiency. The effort is part of NASA’s Sustainable Flight National Partnership to help inform the next generation of ultra-efficient airliners.
GE Aerospace
Inspiring the next generation: A legacy of exploration
NASA’s commitment to STEM education and public engagement continues to inspire future generations of scientists, engineers, and explorers:
- Educational programs:
- NASA offers a wide range of educational programs and resources, including online courses, hands-on activities, and STEM challenges. These programs inspire students to pursue careers in STEM fields and contribute to future space exploration.
- Public engagement:
- NASA engages with the public through a variety of channels, including social media, public events, and virtual experiences. By sharing the excitement of space exploration, NASA inspires people of all ages to dream big and reach for the stars.
- International collaboration:
- NASA fosters international cooperation in space exploration, working with partners from around the world to achieve common goals. By collaborating with other space agencies, NASA can leverage resources, share expertise, and accelerate scientific discovery.
As NASA enters a new era of exploration, the agency remains dedicated to pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and inspiring future generations. With a focus on innovation, collaboration, and scientific discovery, NASA is poised to shape the future of space exploration and benefit humanity for years to come.