Abbas Kanani, Superintendent Pharmacist at Chemist Click Online Pharmacy, walks us through treatments for Alzheimer’s disease, researching the causes, diagnosis, prevention, and cure
Alzheimer’s is a degenerative brain disease that is the most common form of dementia. Dementia is a general term that describes a decline in mental abilities, including memory, reasoning, and communication, which is severe enough to affect daily life.
Research has shown that a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors causes Alzheimer’s disease. The exact causes of Alzheimer’s disease are not yet fully understood, but scientists are working to identify genetic and biochemical markers that may contribute to the development of the disease, and eventually, treatments for Alzheimer’s disease.
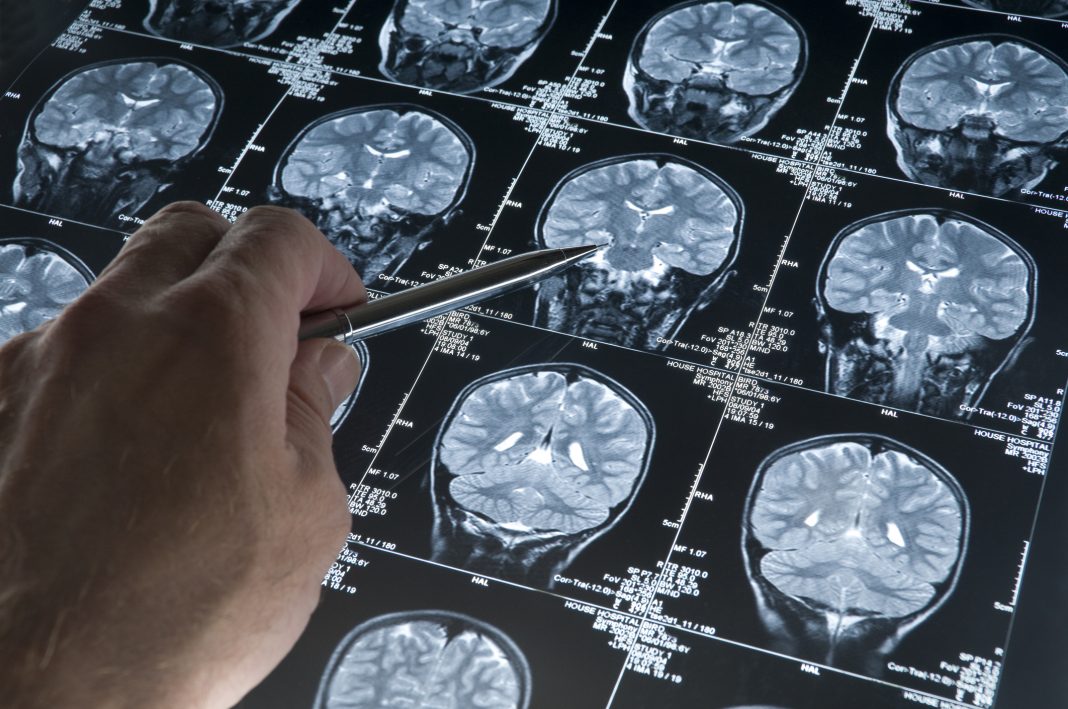
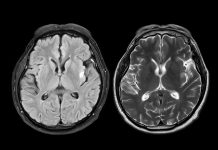
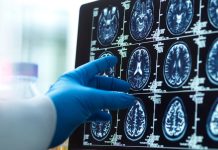
Early and accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for effective treatment and management. In recent years, there have been significant advances in the diagnostic tools used to detect Alzheimer’s disease, including brain imaging, cognitive testing, and biomarker analysis.
Treatments for Alzheimer’s disease are limited, but prevention strategies are key
While there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s, there is evidence that lifestyle modifications, such as exercise, a healthy diet, and cognitive stimulation, may help reduce the risk of developing the disease. In addition, other preventative strategies, such as taking medication to lower cholesterol or blood pressure, may also help to reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Currently, several medications and therapies can help to manage the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, including cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine. However, there is still a significant need for new and more effective treatments for Alzheimer’s disease.
Despite the significant progress that has been made in the understanding of the disease, there is still no cure. Therefore, ongoing research efforts are focused on developing new treatments for Alzheimer’s disease that can slow its progression, as well as identifying the underlying causes.

What are the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease?
The symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease typically develop gradually and worsen over time. One of the earliest and most noticeable symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease is memory loss, particularly difficulty remembering recent events or conversations.
Individuals may have difficulty making decisions, solving problems, or completing familiar tasks. In addition, as the disease progresses, people may become confused or disoriented about the date, time or location, even in familiar surroundings.
Alzheimer’s can also cause mood swings and changes in behaviour, such as increased agitation, anxiety, depression, or paranoia. Some individuals may have trouble speaking, writing, or understanding what others are saying.
Global research, driving risk reduction & early detection
Accelerating global research and driving risk reduction and early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is critical for improving patient outcomes, reducing the economic burden of the disease, and advancing our understanding of this devastating condition.
Early detection and treatment for Alzheimer’s disease can help improve the quality of life and extend the time that individuals can live independently. It also helps slow the disease’s progression and manage its symptoms, delaying the need for more intensive care.
Alzheimer’s is a growing public health challenge. According to WHO, an estimated 47 million people were living with dementia in 2015, which is set to triple by 2050. This is most likely due to an ageing population. This is also likely to have an impact on the global economy. In 2015, the global cost of dementia was 818 billion dollars, which is set to reach 2 trillion dollars by 2050.
Accelerating global research helps to advance our understanding of Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to the development of new treatments, preventions, and eventually a cure. Individuals will also have access to the resources and support they need to manage the disease and maintain their independence for as long as possible.
U.S. federal investments in Alzheimer’s research, better quality care and support services
Securing federal investments in Alzheimer’s research and improving access to better quality care and support services in the U.S. is vital for several reasons. Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most prevalent age-related conditions in the U.S., with an estimated 6 million individuals living with the disease.
Caregivers of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease face a significant physical, emotional, and financial strain, and improving access to care and support services can help to ease this burden. The cost of caring for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease is substantial and is expected to increase significantly in the coming years. Securing federal investments in research and improving access to care and support services can help reduce the disease’s economic burden.
Federal investments also help advance our understanding of the disease, contribute to developing new treatments, and eventually find a cure.
WHO has set a deadline of 2030 to find a cure, and whilst there are breakthroughs, we are a long way off.